Stbd1 promotes glycogen clustering during endoplasmic reticulum stress and supports survival of mouse myoblasts
- PMID: 32958708
- PMCID: PMC7648618
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.244855
Stbd1 promotes glycogen clustering during endoplasmic reticulum stress and supports survival of mouse myoblasts
Abstract
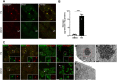
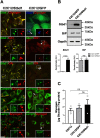
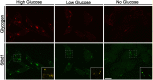
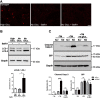
Imbalances in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis provoke a condition known as ER stress and activate the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway, an evolutionarily conserved cell survival mechanism. Here, we show that mouse myoblasts respond to UPR activation by stimulating glycogenesis and the formation of α-amylase-degradable, glycogen-containing ER structures. We demonstrate that the glycogen-binding protein Stbd1 is markedly upregulated through the PERK signalling branch of the UPR pathway and is required for the build-up of glycogen structures in response to ER stress activation. In the absence of ER stress, Stbd1 overexpression is sufficient to induce glycogen clustering but does not stimulate glycogenesis. Glycogen structures induced by ER stress are degraded under conditions of glucose restriction through a process that does not depend on autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Furthermore, we provide evidence that failure to induce glycogen clustering during ER stress is associated with enhanced activation of the apoptotic pathway. Our results reveal a so far unknown response of mouse myoblasts to ER stress and uncover a novel specific function of Stbd1 in this process, which may have physiological implications during myogenic differentiation.This article has an associated First Person interview with the first author of the paper.
Keywords: Apoptosis; ER stress; Glycogen; Glycogen synthase; Glycogenin; UPR.
© 2020. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Axten J. M., Medina J. R., Feng Y., Shu A., Romeril S. P., Grant S. W., Li W. H., Heerding D. A., Minthorn E., Mencken T. et al. (2012). Discovery of 7-methyl-5-(1-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetyl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-5-yl)-7H-p yrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (GSK2606414), a potent and selective first-in-class inhibitor of protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). J. Med. Chem. 55, 7193-7207. 10.1021/jm300713s - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bravo R., Vicencio J. M., Parra V., Troncoso R., Munoz J. P., Bui M., Quiroga C., Rodriguez A. E., Verdejo H. E., Ferreira J. et al. (2011). Increased ER-mitochondrial coupling promotes mitochondrial respiration and bioenergetics during early phases of ER stress. J. Cell Sci. 124, 2143-2152. 10.1242/jcs.080762 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

