Elucidation of the aberrant 3' splice site selection by cancer-associated mutations on the U2AF1
- PMID: 32958768
- PMCID: PMC7505975
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18559-6
Elucidation of the aberrant 3' splice site selection by cancer-associated mutations on the U2AF1
Abstract
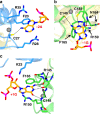
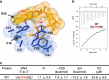
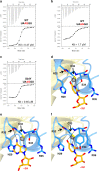
The accurate exclusion of introns by RNA splicing is critical for the production of mature mRNA. U2AF1 binds specifically to the 3´ splice site, which includes an essential AG dinucleotide. Even a single amino acid mutation of U2AF1 can cause serious disease such as certain cancers or myelodysplastic syndromes. Here, we describe the first crystal structures of wild-type and pathogenic mutant U2AF1 complexed with target RNA, revealing the mechanism of 3´ splice site selection, and how aberrant splicing results from clinically important mutations. Unexpected features of this mechanism may assist the future development of new treatments against diseases caused by splicing errors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A splice site-sensing conformational switch in U2AF2 is modulated by U2AF1 and its recurrent myelodysplasia-associated mutation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 4;48(10):5695-5709. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa293. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32343311 Free PMC article.
-
Global analysis of binding sites of U2AF1 and ZRSR2 reveals RNA elements required for mutually exclusive splicing by the U2- and U12-type spliceosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 9;52(3):1420-1434. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1180. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38088204 Free PMC article.
-
Precision analysis of mutant U2AF1 activity reveals deployment of stress granules in myeloid malignancies.Mol Cell. 2022 Mar 17;82(6):1107-1122.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.02.025. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35303483 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing Factor Mutations in Myelodysplasias: Insights from Spliceosome Structures.Trends Genet. 2017 May;33(5):336-348. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Trends Genet. 2017. PMID: 28372848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
U2AF1 in various neoplastic diseases and relevant targeted therapies for malignant cancers with complex mutations (Review).Oncol Rep. 2024 Jan;51(1):5. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8664. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 37975232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IntSplice2: Prediction of the Splicing Effects of Intronic Single-Nucleotide Variants Using LightGBM Modeling.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 19;12:701076. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.701076. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34349788 Free PMC article.
-
Exonic splicing code and coordination of divalent metals in proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 9;52(3):1090-1106. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1161. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38055834 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Threat of Splicing Factor Mutations to Myeloid Malignancies and Potential Therapeutic Modulations.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 15;10(8):1972. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081972. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From benign to pathogenic variants and vice versa: pyrimidine transitions at position -3 of TAG and CAG 3' splice sites.J Hum Genet. 2025 Mar;70(3):125-133. doi: 10.1038/s10038-024-01308-8. Epub 2024 Dec 5. J Hum Genet. 2025. PMID: 39639151 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Caenorhabditis elegans m6A methyltransferase METT10 that regulates SAM homeostasis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Mar 21;51(5):2434-2446. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad081. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36794723 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

