Abrogation of atypical neurogenesis and vascular-derived EphA4 prevents repeated mild TBI-induced learning and memory impairments
- PMID: 32958852
- PMCID: PMC7506550
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-72380-1
Abrogation of atypical neurogenesis and vascular-derived EphA4 prevents repeated mild TBI-induced learning and memory impairments
Abstract
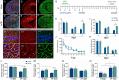
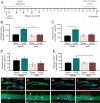
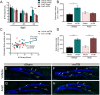
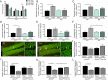
Brain injury resulting from repeated mild traumatic insult is associated with cognitive dysfunction and other chronic co-morbidities. The current study tested the effects of aberrant neurogenesis in a mouse model of repeated mild traumatic brain injury (rmTBI). Using Barnes Maze analysis, we found a significant reduction in spatial learning and memory at 24 days post-rmTBI compared to repeated sham (rSham) injury. Cell fate analysis showed a greater number of BrdU-labeled cells which co-expressed Prox-1 in the DG of rmTBI-injured mice which coincided with enhanced cFos expression for neuronal activity. We then selectively ablated dividing neural progenitor cells using a 7-day continuous infusion of Ara-C prior to rSham or rmTBI. This resulted in attenuation of cFos and BrdU-labeled cell changes and prevented associated learning and memory deficits. We further showed this phenotype was ameliorated in EphA4f./f/Tie2-Cre knockout compared to EphA4f./f wild type mice, which coincided with altered mRNA transcript levels of MCP-1, Cx43 and TGFβ. These findings demonstrate that cognitive decline is associated with an increased presence of immature neurons and gene expression changes in the DG following rmTBI. Our data also suggests that vascular EphA4-mediated neurogenic remodeling adversely affects learning and memory behavior in response to repeated insult.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic gliosis and behavioral deficits in mice following repetitive mild traumatic brain injury.J Neurosurg. 2014 Dec;121(6):1342-50. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.JNS14272. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25267088 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated mild traumatic brain injury produces neuroinflammation, anxiety-like behaviour and impaired spatial memory in mice.Brain Inj. 2018;32(1):113-122. doi: 10.1080/02699052.2017.1380228. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Brain Inj. 2018. PMID: 29156991
-
Long-term cognitive impairment without diffuse axonal injury following repetitive mild traumatic brain injury in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jan 27;378:112268. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112268. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31580914
-
Animal models of closed-skull, repetitive mild traumatic brain injury.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jun;198:109-122. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30822463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A view of obesity as a learning and memory disorder.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2014 Jul;40(3):261-79. doi: 10.1037/xan0000029. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2014. PMID: 25453037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Atypical Neurogenesis, Astrogliosis, and Excessive Hilar Interneuron Loss Are Associated with the Development of Post-Traumatic Epilepsy.Cells. 2023 Apr 25;12(9):1248. doi: 10.3390/cells12091248. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174647 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid MicroRNA Changes in Cognitively Normal Veterans With a History of Deployment-Associated Mild Traumatic Brain Injury.Front Neurosci. 2021 Sep 9;15:720778. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.720778. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34580583 Free PMC article.
-
The endogenous progenitor response following traumatic brain injury: a target for cell therapy paradigms.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Nov;17(11):2351-2354. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.335833. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35535870 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antonius D, et al. Behavioral health symptoms associated with chronic traumatic encephalopathy: a critical review of the literature and recommendations for treatment and research. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2014;26(4):313–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

