Accessing Covid19 epidemic outbreak in Tamilnadu and the impact of lockdown through epidemiological models and dynamic systems
- PMID: 32958973
- PMCID: PMC7494487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108432
Accessing Covid19 epidemic outbreak in Tamilnadu and the impact of lockdown through epidemiological models and dynamic systems
Abstract
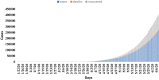
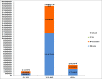
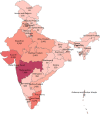
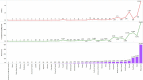
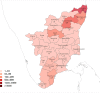
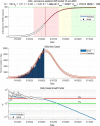
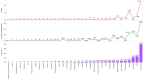
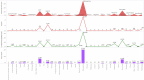
Despite having a small footprint origin, COVID-19 has expanded its clutches to being a global pandemic with severe consequences threatening the survival of the human species. Despite international communities closing their corridors to reduce the exponential spread of the coronavirus. The need to study the patterns of transmission and spread gains utmost importance at the grass-root level of the social structure. To determine the impact of lockdown and social distancing in Tamilnadu through epidemiological models in forecasting the "effective reproductive number" (R0) determining the significance in transmission rate in Tamilnadu after first Covid19 case confirmation on March 07, 2020. Utilizing web scraping techniques to extract data from different online sources to determine the probable transmission rate in Tamilnadu from the rest of the Indian states. Comparing the different epidemiological models (SIR, SIER) in forecasting and assessing the current and future spread of COVID-19. R0 value has a high spike in densely populated districts with the probable flattening of the curve due to lockdown and the rapid rise after the relaxation of lockdown. As of June 03, 2020, there were 25,872 confirmed cases and 208 deaths in Tamilnadu after two and a half months of lockdown with minimal exceptions. As on June 03, 2020, the information published online by the Tamilnadu state government the fatality is at 1.8% (208/11345 = 1.8%) spread with those aged (0-12) at 1437 and 13-60 at 21,899 and 60+ at 2536 the risk of symptomatic infection increases with age and comorbid conditions.
Keywords: Covid-19; Machine learning; SIR model; Tamilnadu.
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Abbey H. An examination of the Reed-Frost theory of epidemics. Hum. Biol. 1952;24(3):201. - PubMed
-
- Barbu V., Iannelli M., Martcheva M. On the controllability of the Lotka–McKendrick model of population dynamics. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2001;253(1):142–165.
-
- Chowell G., Cintrón-Arias A., Del Valle S., Sánchez F., Song B., Hyman J.M., Hethcote H.W., Castillo-Chávez C. Mathematical applications associated with the deliberate release of infectious agents. Contemp. Math. 2006;410:51.
-
- Del Rio C., Malani P.N. COVID-19—new insights on a rapidly changing epidemic. JAMA. 2020;323(14):1339–1340. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
