Imaging for Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Outcome Prediction of Large Vessel Vasculitides
- PMID: 32959107
- PMCID: PMC7505874
- DOI: 10.1007/s11926-020-00955-y
Imaging for Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Outcome Prediction of Large Vessel Vasculitides
Abstract
Purpose of review: To discuss and summarize the latest evidence on imaging techniques in giant cell arteritis (GCA) and Takayasu arteritis (TAK). This is a report on the performance of ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18-FDG-PET), and other emerging imaging techniques in diagnosis, outcome prediction, and monitoring of disease activity.
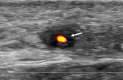
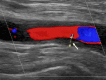
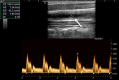
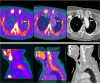
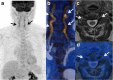
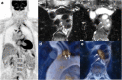
Recent findings: Imaging techniques have gained an important role for diagnosis of large vessel vasculitides (LVV). As signs of vasculitis, US, MRI, and CT show a homogeneous arterial wall thickening, which is mostly concentric. PET displays increased FDG uptake in inflamed artery walls. US is recommended as the initial imaging modality in GCA. MRI and PET/CT may also detect vasculitis of temporal arteries. For TAK, MRI is recommended as the first imaging modality as it provides a good overview without radiation. Extracranial LVV can be confirmed by all four modalities. In addition, MRI and PET/CT provide consistent examination of the aorta and its branches. New techniques such as contrast-enhanced ultrasound, PET/MRI, and auxiliary methods such as "computer-assisted quantitative analysis" have emerged and need to be further validated. Imaging has partly replaced histology for confirming LVV. Provided experience and adequate training, US, MRI, CT, or PET provide excellent diagnostic accuracy. Imaging results need to complement history and clinical examination. Ongoing studies are evaluating the role of imaging for monitoring and outcome measurement.
Keywords: 18F- fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography; Computed tomography; Diagnosis; Giant cell arteritis; Imaging; Large vessel vasculitis; Magnetic resonance imaging; Outcome; Takayasu arteritis; Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imaging in large-vessel vasculitis.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Dec;34(6):101589. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2020.101589. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32948434 Review.
-
[Imaging diagnostics in large vessel vasculitis].Z Rheumatol. 2019 Nov;78(9):847-858. doi: 10.1007/s00393-019-00711-3. Z Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31541286 German.
-
[News on the imaging of large vessel vasculitis].Z Rheumatol. 2024 Dec;83(10):800-811. doi: 10.1007/s00393-024-01565-0. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Z Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39271483 Review. German.
-
Imaging in Large Vessel Vasculitides.Rofo. 2019 Dec;191(12):1083-1090. doi: 10.1055/a-0896-2833. Epub 2019 May 16. Rofo. 2019. PMID: 31096287 Review. English.
-
EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice summary.Radiol Med. 2019 Oct;124(10):965-972. doi: 10.1007/s11547-019-01058-0. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Radiol Med. 2019. PMID: 31254221 Review.
Cited by
-
Atypical Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) in a Patient with Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis.Curr Health Sci J. 2021 Apr-Jun;47(2):306-309. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.47.02.23. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Curr Health Sci J. 2021. PMID: 34765253 Free PMC article.
-
18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography Findings of Polymyalgia Rheumatica in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 8;12(22):6983. doi: 10.3390/jcm12226983. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38002597 Free PMC article.
-
Tocilizumab in refractory Caucasian Takayasu's arteritis: a multicenter study of 54 patients and literature review.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021 Jun 18;13:1759720X211020917. doi: 10.1177/1759720X211020917. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021. PMID: 34211589 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosing vasculitis with ultrasound: findings and pitfalls.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2024 Jun 5;16:1759720X241251742. doi: 10.1177/1759720X241251742. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2024. PMID: 38846756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging Tests in the Early Diagnosis of Giant Cell Arteritis.J Clin Med. 2021 Aug 20;10(16):3704. doi: 10.3390/jcm10163704. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34442002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stone JR, Bruneval P, Angelini A, Bartoloni G, Basso C, Batoroeva L, et al. Consensus statement on surgical pathology of the aorta from the Society for Cardiovascular Pathology and the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology: I. Inflammatory diseases. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2015;24(5):267–278. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2015.05.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

