Return to Physical Activity After High Tibial Osteotomy or Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Pooling Data Analysis
- PMID: 32960075
- PMCID: PMC8020302
- DOI: 10.1177/0363546520948861
Return to Physical Activity After High Tibial Osteotomy or Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Pooling Data Analysis
Abstract
Background: The 2 most common definitive surgical interventions currently performed for the treatment of medial osteoarthritis of the knee are medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy (HTO) and medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA). Research exists to suggest that physically active patients may be suitably indicated for either procedure despite HTO being historically indicated in active patients and UKA being more appropriate for sedentary individuals.
Purpose: To help consolidate the current indications for both procedures regarding physical activity and to ensure that they are based on the best information presently available.
Study design: Systematic review.
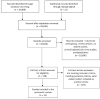
Methods: A search of the literature via the MEDLINE, Embase, and PubMed databases was conducted independently by 2 reviewers in accordance with the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Meta-Analyses) guidelines. Studies that reported patient physical activity levels with the Tegner activity score were eligible for inclusion. Patient demographics, operative variables, and patient-reported outcome scores were abstracted from the included studies.
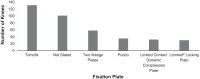
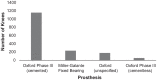
Results: Thirteen eligible studies were included, consisting of 401 knees that received HTO (399 patients) and 1622 that received UKA (1400 patients). The patients' mean age at surgery was 48.4 years for the HTO group and 60.6 years for the UKA group. Mean follow-up was 46.6 months (HTO) and 53.4 months (UKA). All outcome scores demonstrated an equal or improved score for activity and knee function regardless of the operation performed. Operative variables during HTO had a larger effect on outcome than during UKA.
Conclusion: Patients who underwent HTO were more physically active pre- and postoperatively, but patients undergoing UKA experienced an overall greater increase in their physical activity levels and knee function according to Tegner and Lysholm scores. Activity after HTO may be influenced by operative factors such as the implant used and the decision to include a graft material in the osteotomy gap, although this requires further research. Some studies found that patients were able to return to physical activity postoperatively despite having an age or body mass index that would traditionally be a relative contraindication for HTO or UKA.
Keywords: high tibial osteotomy; indications; knee replacement; outcome; physical activity; quality of life; return to sport; unicompartmental knee arthroplasty; unicondylar knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
One or more of the authors has declared the following potential conflict of interest or source of funding: J.B. is undertaking a PhD project (University of Winchester) that has been funded by RTI Surgical Inc, which provided materials for other studies within the project; the present article forms a part of the project. S.J. oversees a fund that has received monies from Össur and NewClip Technics for related research. This fund also received the sponsorship from RTI Surgical Inc that has funded the PhD project being undertaken by J.B. A.J.W. is a consultant for NewClip Technics and receives financial reimbursement from the company. AOSSM checks author disclosures against the Open Payments Database (OPD). AOSSM has not conducted an independent investigation on the OPD and disclaims any liability or responsibility relating thereto.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy allows better outcomes than unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in patients expecting to return to impact sports.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020 Dec;28(12):3849-3857. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-05857-1. Epub 2020 Feb 1. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020. PMID: 32008058
-
Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty is associated with lower pain levels but inferior range of motion, compared with high tibial osteotomy: a systematic overview of meta-analyses.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Sep 24;17(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03319-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 36153554 Free PMC article.
-
Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty is superior to high tibial osteotomy for the treatment of medial unicompartmental osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jul 29;101(30):e29576. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029576. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35905249 Free PMC article.
-
Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty vs High Tibial Osteotomy for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Arthroplasty. 2018 Mar;33(3):952-959. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.10.025. Epub 2017 Dec 2. J Arthroplasty. 2018. PMID: 29203354
-
Predictive factors for satisfaction after contemporary unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy in isolated medial femorotibial osteoarthritis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019 Feb;105(1):77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Dec 1. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 30509622
Cited by
-
Osteotomy Around the Knee: The Surgical Treatment of Osteoarthritis.Orthop Surg. 2021 Jul;13(5):1465-1473. doi: 10.1111/os.13021. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 34110088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Tibial Osteotomy Versus Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty for Unicompartmental Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Indian J Orthop. 2022 Mar 21;56(6):973-982. doi: 10.1007/s43465-022-00620-9. eCollection 2022 Jun. Indian J Orthop. 2022. PMID: 35669023 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-articular injections in sport-active patients with degenerative cartilage lesions or osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review.J Exp Orthop. 2023 Nov 8;10(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s40634-023-00674-0. J Exp Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37938446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BEST PROSTHESIS FOR UNICOMPARTMENTAL KNEE ARTHROSIS: FIXED OR MOBILE?Acta Ortop Bras. 2025 Feb 3;33(1):e285052. doi: 10.1590/1413-785220253301e285052. eCollection 2025. Acta Ortop Bras. 2025. PMID: 39927313 Free PMC article.
-
A novel biplanar medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy: the Z-shaped technique. A case series at 7.2 years follow-up.J Orthop Traumatol. 2021 Dec 14;22(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s10195-021-00617-4. J Orthop Traumatol. 2021. PMID: 34905126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anagnostakos K, Mosser P, Kohn D. Infections after high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(1):161-169. - PubMed
-
- Bastard C, Mirouse G, Potage D, et al.. Return to sports and quality of life after high tibial osteotomy in patients under 60 years of age. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(8):1189-1191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

