CT features of feline lipiduria and renal cortical lipid deposition
- PMID: 32960133
- PMCID: PMC8008399
- DOI: 10.1177/1098612X20957161
CT features of feline lipiduria and renal cortical lipid deposition
Abstract
Objectives: The aims of this study were to document the presence and prevalence of feline lipiduria and renal lipid deposition on CT, and to search for associations between the presence of lipiduria and sex, urinary tract abnormalities and urolithiasis.
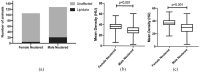
Methods: The CT examinations of 252 cats were reviewed for the presence of an antigravitational hypodense bubble in the urinary bladder with density values between -180 Hounsfield units (HU) and -20 HU. To identify associations between lipiduria and sex, urinary tract abnormalities and urolithiasis, Fisher's exact test was used. Renal cortical density measurement was performed in all cats. The Mann-Whitney test was performed to compare renal cortical density between lipiduric and unaffected cats.
Results: A total of 27 domestic cats (10.7%) had CT evidence of lipiduria. Lipiduric cats had a significantly lower renal cortical density than unaffected cats (P <0.01). Male neutered cats had a significantly higher frequency of lipiduria and lower renal cortical density compared with female neutered cats (P <0.01). There was no significant difference between the groups regarding renal, ureteral or urethral abnormalities.
Conclusions and relevance: Lipiduria is a common physiological phenomenon in cats that can be detected on routine CT examinations. Decreased renal cortical density is associated with lipiduria. This may aid in the diagnosis of feline lipiduria and help to differentiate its presence from other pathological depositions and excretions.
Keywords: CT; fat droplets; fat-fluid level; lipiduria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Fry MM. Urinalysis. In: Bartges J, Polzin D. (eds). Nephrology and urology of small animals. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell, 2011, pp 46–57.
-
- Skeldon N, Ristić J. Urinalysis. In: Villiers E, Ristić J. (eds). BSAVA manual of canine and feline clinical pathology. 3rd ed. Quedgeley: British Small Animal Veterinary Association, 2016, pp 183–218.
-
- Martin RS, Small DM. Physicochemical characterization of the urinary lipid from humans with nephrotic syndrome. J Lab Clin Med 1984; 103: 798–810. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

