Neuron-specific deletion of presenilin enhancer2 causes progressive astrogliosis and age-related neurodegeneration in the cortex independent of the Notch signaling
- PMID: 32961023
- PMCID: PMC7816208
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.13454
Neuron-specific deletion of presenilin enhancer2 causes progressive astrogliosis and age-related neurodegeneration in the cortex independent of the Notch signaling
Abstract
Introduction: Presenilin enhancer2 (Pen-2) is an essential subunit of γ-secretase, which is a key protease responsible for the cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) and Notch. Mutations on Pen-2 cause familial Alzheimer disease (AD). However, it remains unknown whether Pen-2 regulates neuronal survival and neuroinflammation in the adult brain.
Methods: Forebrain neuron-specific Pen-2 conditional knockout (Pen-2 cKO) mice were generated for this study. Pen-2 cKO mice expressing Notch1 intracellular domain (NICD) conditionally in cortical neurons were also generated.
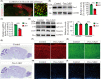
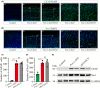
Results: Loss of Pen-2 causes astrogliosis followed by age-dependent cortical atrophy and neuronal loss. Loss of Pen-2 results in microgliosis and enhanced inflammatory responses in the cortex. Expression of NICD in Pen-2 cKO cortices ameliorates neither neurodegeneration nor neuroinflammation.
Conclusions: Pen-2 is required for neuronal survival in the adult cerebral cortex. The Notch signaling may not be involved in neurodegeneration caused by loss of Pen-2.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; astrogliosis; microgliosis; neurodegeneration; presenilin enhancer2.
© 2020 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A, et al. Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 2011;377(9770):1019‐1031. - PubMed
-
- Palmer AM. Neurochemical studies of Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegeneration. 1996;5(4):381‐391. - PubMed
-
- Levylahad E, Wasco W, Poorkaj P, et al. Candidate gene for the chromosome‐1 familial Alzheimers‐disease locus. Science. 1995;269(5226):973‐977. - PubMed
-
- Schellenberg GD, Bird TD, Wijsman EM, et al. Genetic‐linkage evidence for a familial Alzheimers‐disease locus on chromosome‐14. Science. 1992;258(5082):668‐671. - PubMed
-
- Goate A, Chartierharlin MC, Mullan M, et al. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimers‐disease. Nature. 1991;349(6311):704‐706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

