Performance verification of anti-SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody detection by using four chemiluminescence immunoassay systems
- PMID: 32961061
- PMCID: PMC7672672
- DOI: 10.1177/0004563220963847
Performance verification of anti-SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody detection by using four chemiluminescence immunoassay systems
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the analytical performance of seven kits for detecting IgM/IgG antibodies against coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) by using four chemiluminescence immunoassay systems.
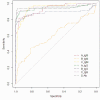
Methods: Fifty patients diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection and 130 controls without coronavirus infection from the General Hospital of Chongqing were enrolled in the current retrospective study. Four chemiluminescence immunoassay systems, including seven IgM/IgG antibody detection kits for SARS-CoV-2 (A_IgM, A_IgG, B_IgM, B_IgG, C_IgM, C_IgG and D_Ab), were employed to detect antibody concentrations. The chi-square test, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and Youden's index were determined to verify the cut-off value of each detection system.
Results: The repeatability verification results of the A, B, C and D systems are all qualified. D_Ab performed best (92% sensitivity and 99.23% specificity), and B_IgM performed worse than the other systems. Except for the A_IgM and C_IgG systems, the optimal diagnostic thresholds and cut-off values of the other kits and their recommendations are inconsistent with each other. B_IgM had the worst AUC, and C_IgG had the best diagnostic accuracy. More importantly, the B_IgG system had the highest false-positive rate for testing patients with AIDS, tumours and pregnancies. The A_IgM system test showed the highest false-positive rates among elderly individuals over 90 years old. COVID-2019 IgM/IgG antibody test systems exhibit performance differences.
Conclusions: The Innodx Biotech Total Antibody serum diagnosis kit is the most reliable detection system for anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, which can be used together with nucleic acid tests as an alternative method for SARS-CoV-2 detecting.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody; chemiluminescence immunoassay; performance verification.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- P.R.China NHCoNovel corona virus pneumonia diagnosis and treatment guideline (trial version 7). [EB/OL], www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/zhengcwj/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb1989.shtml (2020, accessed 24 September 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous