Single-Cell Analyses Identify Brain Mural Cells Expressing CD19 as Potential Off-Tumor Targets for CAR-T Immunotherapies
- PMID: 32961131
- PMCID: PMC7640763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.022
Single-Cell Analyses Identify Brain Mural Cells Expressing CD19 as Potential Off-Tumor Targets for CAR-T Immunotherapies
Abstract
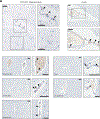
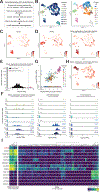
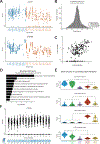
CD19-directed immunotherapies are clinically effective for treating B cell malignancies but also cause a high incidence of neurotoxicity. A subset of patients treated with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells or bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) antibodies display severe neurotoxicity, including fatal cerebral edema associated with T cell infiltration into the brain. Here, we report that mural cells, which surround the endothelium and are critical for blood-brain-barrier integrity, express CD19. We identify CD19 expression in brain mural cells using single-cell RNA sequencing data and confirm perivascular staining at the protein level. CD19 expression in the brain begins early in development alongside the emergence of mural cell lineages and persists throughout adulthood across brain regions. Mouse mural cells demonstrate lower levels of Cd19 expression, suggesting limitations in preclinical animal models of neurotoxicity. These data suggest an on-target mechanism for neurotoxicity in CD19-directed therapies and highlight the utility of human single-cell atlases for designing immunotherapies.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests C.H.J. and A.D.P. report intellectual property licensed to Novartis and Tmunity Therapeutics related to CAR-T cells. K.R.P., A.T.S., H.Y.C., D.M., A.D.P., and C.H.J. are listed as inventors on patent applications filed by Stanford University and the University of Pennsylvania. K.R.P. is a consultant for Maze Therapeutics. A.T.S. is a scientific founder of Immunai and receives research funding from Arsenal Biosciences. H.Y.C. is a co-founder of Accent Therapeutics and Boundless Bio and an advisor to 10x Genomics, Arsenal Biosciences, and Spring Discovery.
Figures

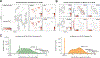


Comment in
-
Brain Mural Cells Express CAR T-cell Target.Cancer Discov. 2020 Dec;10(12):1781-1782. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2020-095. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 33097477
-
Using single-cell analysis to predict CAR T cell outcomes.Nat Med. 2020 Dec;26(12):1813-1814. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-01157-w. Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 33230341 No abstract available.
References
-
- Armulik A, Genové G, Mäe M, Nisancioglu MH, Wallgard E, Niaudet C, He L, Norlin J, Lindblom P, Strittmatter K, et al. (2010). Pericytes regulate the blood–brain barrier. Nature 468, 557–561. - PubMed
-
- Boroujerdi A, Tigges U, Welser-Alves JV, and Milner R (2014). Isolation and culture of primary pericytes from mouse brain. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 1135, 383–392. - PubMed
-
- Braig F, Brandt A, Goebeler M, Tony H-P, Kurze A-K, Nollau P, Bumm T, Böttcher S, Bargou RC, and Binder M (2017). Resistance to anti-CD19/CD3 BiTE in acute lymphoblastic leukemia may be mediated by disrupted CD19 membrane trafficking. Blood 129, 100–104. - PubMed
-
- Brentjens RJ, Latouche J-B, Santos E, Marti F, Gong MC, Lyddane C, King PD, Larson S, Weiss M, Rivière I, et al. (2003). Eradication of systemic B-cell tumors by genetically targeted human T lymphocytes co-stimulated by CD80 and interleukin-15. Nat. Med 9, 279–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RM1 HG007735/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P41 EB015893/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS097305/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH105989/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HG007735/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA230188/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS062684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042645/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA209919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- IK2 BX004183/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 AI091627/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

