Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 32961245
- PMCID: PMC7833189
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.09.002
Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
Rationale & objective: Outcomes of patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and acute kidney injury (AKI) are not well understood. The goal of this study was to investigate the survival and kidney outcomes of these patients.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
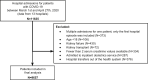
Setting & participants: Patients (aged≥18 years) hospitalized with COVID-19 at 13 hospitals in metropolitan New York between March 1, 2020, and April 27, 2020, followed up until hospital discharge.
Exposure: AKI.
Outcomes: Primary outcome: in-hospital death.
Secondary outcomes: requiring dialysis at discharge, recovery of kidney function.
Analytical approach: Univariable and multivariable time-to-event analysis and logistic regression.
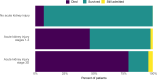
Results: Among 9,657 patients admitted with COVID-19, the AKI incidence rate was 38.4/1,000 patient-days. Incidence rates of in-hospital death among patients without AKI, with AKI not requiring dialysis (AKI stages 1-3), and with AKI receiving dialysis (AKI 3D) were 10.8, 31.1, and 37.5/1,000 patient-days, respectively. Taking those without AKI as the reference group, we observed greater risks for in-hospital death for patients with AKI 1-3 and AKI 3D (HRs of 5.6 [95% CI, 5.0-6.3] and 11.3 [95% CI, 9.6-13.1], respectively). After adjusting for demographics, comorbid conditions, and illness severity, the risk for death remained higher among those with AKI 1-3 (adjusted HR, 3.4 [95% CI, 3.0-3.9]) and AKI 3D (adjusted HR, 6.4 [95% CI, 5.5-7.6]) compared with those without AKI. Among patients with AKI 1-3 who survived, 74.1% achieved kidney recovery by the time of discharge. Among those with AKI 3D who survived, 30.6% remained on dialysis at discharge, and prehospitalization chronic kidney disease was the only independent risk factor associated with needing dialysis at discharge (adjusted OR, 9.3 [95% CI, 2.3-37.8]).
Limitations: Observational retrospective study, limited to the NY metropolitan area during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusions: AKI in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 was associated with significant risk for death.
Keywords: AKI-on-CKD; COVID-19 outcomes; Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); acute kidney injury (AKI); acute renal failure (ARF); death; dialysis; hospitalization; in-hospital mortality; kidney replacement therapy (KRT); recovery; renal prognosis; renal recovery; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Copyright © 2020 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
COVID-19: The Kidneys Tell a Tale.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Feb;77(2):175-177. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.11.001. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 33342610 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chan L, Chaudhary K, Saha A, et al. Acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 [published online ahead of print 2020]. J Am Soc Nephrol. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020050615 - DOI
-
- Epic Health Research Network Acute kidney injury in admitted COVID-19 patients – Epic Health Research Network. Published July 1, 2020. Accessed July 11, 2020. https://www.ehrn.org/acute-kidney-injury-in-admitted-covid-19-patients/
-
- Ricci Z., Cruz D., Ronco C. The RIFLE criteria and mortality in acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney Int. 2008;73(5):538–546. - PubMed
-
- Silver S.A., Long J., Zheng Y., Chertow G.M. Cost of acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(2):70–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

