Identification of Antitumor Constituents in Toad Venom by Spectrum-Effect Relationship Analysis and Investigation on Its Pharmacologic Mechanism
- PMID: 32961837
- PMCID: PMC7571126
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184269
Identification of Antitumor Constituents in Toad Venom by Spectrum-Effect Relationship Analysis and Investigation on Its Pharmacologic Mechanism
Abstract
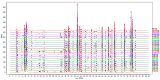
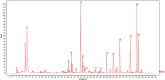
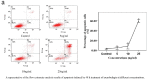
(1) Background: Toad venom (Bufonis Venenum, known as 'Chansu' in Chinese), the secretion of the ear-side gland and skin gland of Bufo gargarizans cantor or Duttaphrynus melanostictus Schneider, has been utilized to treat several diseases in China for thousands of years. However, due to the chemical variability of the components, systematic chemical composition and the key pharmacophores in toad venom have not yet fully understood. Besides, it contains a variety of effective compounds with different physiological activity and chemotypes, mainly including alkaloids, bufogenins, bufotoxins, and so on. The recent pharmacological researches have demonstrated that several bufogenins have remarkable pharmacological effects, such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic effects, and anti-tumor effects. Aim of the study: To identify the bioactive compounds and pharmacophores originating from toad venom based on analyzing spectrum-effect relationship by chemometrics and to explore the anti-cancer mechanism primarily. (2) Materials and methods: Fingerprint of the 21 batches of samples was established using HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography). The anti-tumor activity of extracts were determined by in-vitro assays. Chemometric analysis was used to establish the spectrum-effect model and screen for active ingredients. Pharmacodynamic tests for the screened active compound monomers were conducted with in-vitro assays. Further anti-tumor mechanisms were investigated using western blot and flow cytometry. (3) Results: The established spectrum-effect model has satisfactory fitting effect and predicting accuracy. The inhibitory effect of major screened compounds on lung carcinoma cells A549 were validated in vitro, demonstrating that arenobufagin, telocinobufogenin, and cinobufotalin had significant anti-tumor effects. Through further investigation of the mechanism by western blotting and flow cytometry, we elucidated that arenobufagin induces apoptosis in A549 cells with the enhanced expression of cleaved PARP (poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase). These results may provide valuable information for further structural modification of bufadienolides to treat lung cancer and a method for discovery of anti-tumor active compounds. Conclusions: Our research offers a more scientific method for screening the principal ingredients dominating the pharmacodynamic function. These screened compounds (arenobufagin, etc.) were proven to induce apoptosis by overactivation of the PARP-pathway, which may be utilized to make BRCA (breast cancer susceptibility gene) mutant cancer cells more vulnerable to DNA damaging agents and kill them.
Keywords: apoptosis; chemometrics; spectrum-effect relationship; toad venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Multi-component identification and target cell-based screening of potential bioactive compounds in toad venom by UPLC coupled with high-resolution LTQ-Orbitrap MS and high-sensitivity Qtrap MS.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Jul;410(18):4419-4435. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1097-4. Epub 2018 Apr 28. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29704033
-
Chemical profiling and cytotoxicity assay of bufadienolides in toad venom and toad skin.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jul 1;187:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.062. Epub 2016 Apr 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27063985
-
Comparative Analysis of Hydrophilic Ingredients in Toad Skin and Toad Venom Using the UHPLC-HR-MS/MS and UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Methods Together with the Anti-Inflammatory Evaluation of Indolealkylamines.Molecules. 2018 Dec 27;24(1):86. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010086. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30591646 Free PMC article.
-
Combinational Antitumor Strategies Based on the Active Ingredients of Toad Skin and Toad Venom.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Aug 9;18:3549-3594. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S469832. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39139676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toad venom: A comprehensive review of chemical constituents, anticancer activities, and mechanisms.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2021 Jul;354(7):e2100060. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202100060. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2021. PMID: 33887066 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemistry and the Potential Antiviral, Anticancer, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Cardiotonic Steroids Derived from Toads.Molecules. 2022 Oct 5;27(19):6586. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196586. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Protein Quality Markers in Toad Venom from Bufo gargarizans.Molecules. 2023 Apr 21;28(8):3628. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083628. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110862 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, Identification and Chemical Modification of Bufadienolides from Bufo melanostictus Schneider and Their Cytotoxic Activities against Prostate Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2024 Mar 31;29(7):1571. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071571. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611850 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization and Spectrum-Effect Analysis of Ultrasonically Extracted Antioxidant Flavonoids from Persicae Ramulus.Molecules. 2024 Aug 15;29(16):3860. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163860. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202938 Free PMC article.
-
Advances on Delivery System of Active Ingredients of Dried Toad Skin and Toad Venom.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jul 18;19:7273-7305. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S469742. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39050871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

