IIAEK Targets Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase (IAP) to Improve Cholesterol Metabolism with a Specific Activation of IAP and Downregulation of ABCA1
- PMID: 32961978
- PMCID: PMC7551322
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12092859
IIAEK Targets Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase (IAP) to Improve Cholesterol Metabolism with a Specific Activation of IAP and Downregulation of ABCA1
Abstract
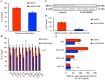
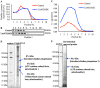
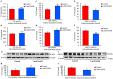
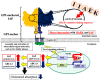
IIAEK (Ile-Ile-Ala-Glu-Lys, lactostatin) is a novel cholesterol-lowering pentapeptide derived from bovine milk β-lactoglobulin. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the IIAEK-mediated suppression of intestinal cholesterol absorption are unknown. Therefore, we evaluated the effects of IIAEK on intestinal cholesterol metabolism in a human intestinal model using Caco-2 cells. We found that IIAEK significantly reduced the expression of intestinal cholesterol metabolism-associated genes, particularly that of the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1). Subsequently, we chemically synthesized a novel molecular probe, IIXEK, which can visualize a complex of target proteins interacting with photoaffinity-labeled IIAEK by fluorescent substances. Through photoaffinity labeling and MS analysis with IIXEK for the rat small intestinal mucosa and intestinal lipid raft fractions of Caco-2 cells, we identified intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IAP) as a specific molecule interacting with IIAEK and discovered the common IIAEK-binding amino acid sequence, GFYLFVEGGR. IIAEK significantly increased IAP mRNA and protein levels while decreasing ABCA1 mRNA and protein levels in Caco-2 cells. In conclusion, we found that IIAEK targets IAP to improve cholesterol metabolism via a novel signaling pathway involving the specific activation of IAP and downregulation of intestinal ABCA1.
Keywords: ABCA1; Caco-2 cells; IIAEK; alkaline phosphatase; cholesterol; photoaffinity labeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ginsberg H.N., Barr S.L., Gilbert A., Karmally W., Deckelbaum R., Kaplan K., Ramakrishnan R., Holleran S., Dell R.B. Reduction of plasma cholesterol levels in normal men on an American Heart Association step 1 diet or a step 1 diet with added monounsaturated fat. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990;322:574–579. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003013220902. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hori G., Wang M.F., Chan Y.C., Komatsu T., Wong Y., Chen T.H., Yamamoto K., Nagaoka S., Yamamoto S. Soy protein hydrolysate with bound phospholipids reduces serum cholesterol levels in hypercholesterolemic adult male volunteers. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001;65:72–78. doi: 10.1271/bbb.65.72. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Spady D.K., Cuthbert J.A., Willard M.N., Meidell R.S. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a gene encoding cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase into hamsters increases hepatic enzyme activity and reduces plasma total and low density lipoprotein cholesterol. J. Clin. Investig. 1995;96:700–709. doi: 10.1172/JCI118113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Spady D.K., Cuthbert J.A., Willard M.N., Meidell R.S. Overexpression of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A) in mice lacking the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene. LDL transport and plasma LDL concentrations are reduced. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:126–132. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.1.126. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

