Cytotoxic Properties of 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Derivatives-A Review
- PMID: 32962192
- PMCID: PMC7570754
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184309
Cytotoxic Properties of 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Derivatives-A Review
Abstract
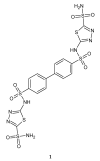
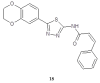
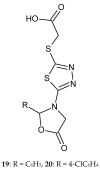
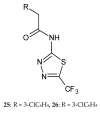
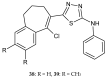
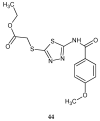
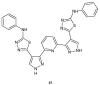
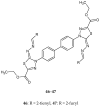
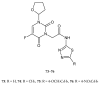
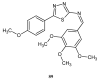
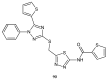
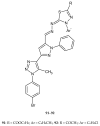
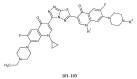
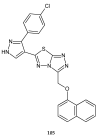
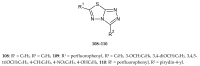
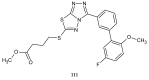
During recent years, small molecules containing five-member heterocyclic moieties have become the subject of considerable growing interest for designing new antitumor agents. One of them is 1,3,4-thiadiazole. This study is an attempt to collect the 1,3,4-thiadiazole and its derivatives, which can be considered as potential anticancer agents, reported in the literature in the last ten years.
Keywords: anticancer activity; cytotoxicity; thiadiazole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures


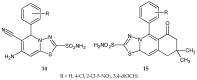






















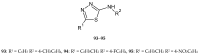
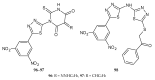
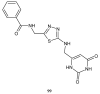







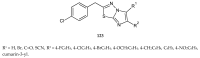
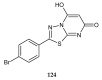
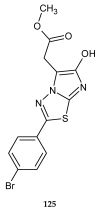


Similar articles
-
Human Cancer Cell Line Based Approach of 1,3,4-thiadiazole and its Fused Ring: A Comprehensive Review.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(4):500-523. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666161013150151. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27745547 Review.
-
Novel diosgenin derivatives containing 1,3,4-oxadiazole/thiadiazole moieties as potential antitumor agents: Design, synthesis and cytotoxic evaluation.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Jan 15;186:111897. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111897. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31761382
-
Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Thiadiazole Containing Thiourea, Benzothiazole and Imidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole Scaffolds.Med Chem. 2021;17(7):750-765. doi: 10.2174/1573406416666200519085626. Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32427086
-
Lemon Juice as a Biocatalyst Under Ultrasound Irradiation: Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of 2-amino 1,3,4-thiadiazoles.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(11):1379-1386. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200409143513. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32271700
-
1,3,4-Thiadiazole Based Anticancer Agents.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016;16(10):1301-14. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666160628100936. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27484056 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitrogen-Containing Heterocycles as Significant Molecular Scaffolds for Medicinal and Other Applications.Molecules. 2021 Jul 30;26(15):4617. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154617. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361770 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen-fused Heterocycles: Empowering Anticancer Drug Discovery.Med Chem. 2024;20(4):369-384. doi: 10.2174/0115734064278334231211054053. Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38192143 Review.
-
Recent Developments of 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Compounds as Anticancer Agents.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;18(4):580. doi: 10.3390/ph18040580. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40284015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel thiadiazole derivatives as potent VEGFR-2 inhibitors: a comprehensive in vitro and in silico study.RSC Adv. 2024 Nov 6;14(48):35505-35519. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04158e. eCollection 2024 Nov 4. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39507692 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles Stabilized with Phosphorus-Containing Heterocyclic Surfactants: Synthesis, Physico-Chemical Properties, and Biological Activity Determination.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jul 22;11(8):1883. doi: 10.3390/nano11081883. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34443714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalidhar U., Kau A. 1, 3, 4-Thiadiazole derivatives and their biological activities: A Review. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2011;2:1091–1106.
-
- Chen C.J., Song B.A., Yang S., Xu G.F., Bhadury P.S., Jin L.H., Hu D.Y., Li Z.Q., Liu F., Xue W., et al. Synthesis and antifungal activities of 5-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-sulfonyl-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole and 5-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-sulfonyl-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007;15:3981–3989. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.04.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hafez H.N., Hegab M.I., Ahmed-Farag I.S., El-Gazzar A.B.A. A facile regioselective synthesis of novel spiro-thioxanthene and spiro-xanthene-9′, 2-[1,3,4] thiadiazole derivatives as potential analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008;18:4538–4543. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.07.042. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

