The Impact of Antifungal Prophylaxis in Lung Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 32962402
- PMCID: PMC7919156
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-267OC
The Impact of Antifungal Prophylaxis in Lung Transplant Recipients
Abstract
Rationale: Many lung transplant centers prescribe antifungal medications after transplantation to prevent invasive fungal infections (IFIs); however, the effectiveness of antifungal prophylaxis at reducing the risk of all-cause mortality or IFI has not been established.Objectives: We aimed to evaluate the effect of antifungal prophylaxis on all-cause mortality and IFI in lung transplant patients.Methods: Using administrative claims data, we identified adult patients who underwent lung transplantation between January 1, 2005, and December 31, 2018. Propensity score analysis using inverse probability treatment-weighting approach was used to balance the differences in baseline characteristics between those receiving antifungal prophylaxis and those not receiving antifungal prophylaxis. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to compare rates of all-cause mortality and IFI in both groups.Results: We identified 662 lung transplant recipients (LTRs) (387 received prophylaxis and 275 did not). All-cause mortality was significantly lower in those receiving antifungal prophylaxis compared with those not receiving antifungal prophylaxis (event rate per 100 person-years, 8.36 vs. 19.49; hazard ratio, 0.43; 95% confidence interval, 0.26-0.71; P = 0.003). Patients receiving antifungal prophylaxis had a lower rate of IFI compared with those not receiving prophylaxis (event rate per 100 person-years, 14.94 vs. 22.37; hazard ratio, 0.68; 95% confidence interval, 0.44-1.05; P = 0.079), but did not reach statistical significance.Conclusions: In this real-world analysis, antifungal prophylaxis in LTRs was associated with reduced all-cause mortality compared with those not receiving antifungal prophylaxis. Rates of IFI were also lower in those receiving prophylaxis, but this was not statistically significant in our primary analysis.
Keywords: Aspergillus; antifungal prophylaxis; fungal infections; lung transplant; triazole.
Figures
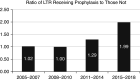

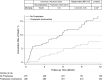
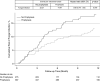

Comment in
-
Antifungal Prophylaxis.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021 Oct;18(10):1755-1756. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202103-300LE. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021. PMID: 33901407 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply: Antifungal Prophylaxis.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021 Oct;18(10):1755-1756. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202104-445LE. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2021. PMID: 33901414 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chan KM, Allen SA. Infectious pulmonary complications in lung transplant recipients. Semin Respir Infect. 2002;17:291–302. - PubMed
-
- Arthurs SK, Eid AJ, Deziel PJ, Marshall WF, Cassivi SD, Walker RC, et al. The impact of invasive fungal diseases on survival after lung transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2010;24:341–348. - PubMed
-
- Pappas PG, Alexander BD, Andes DR, Hadley S, Kauffman CA, Freifeld A, et al. Invasive fungal infections among organ transplant recipients: results of the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network (TRANSNET) Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:1101–1111. - PubMed
-
- Cornely OA, Maertens J, Winston DJ, Perfect J, Ullmann AJ, Walsh TJ, et al. Posaconazole vs. fluconazole or itraconazole prophylaxis in patients with neutropenia. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:348–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

