SLC6A4 gene L/S polymorphism and susceptibility to pulmonary arterial hypertension: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 32962488
- PMCID: PMC7520923
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060520935309
SLC6A4 gene L/S polymorphism and susceptibility to pulmonary arterial hypertension: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association between the solute carrier family 6 member 4 (SLC6A4) gene L/S polymorphism and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
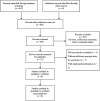
Methods: The relevant literature was retrieved from the PubMed® database and the data were extracted. STATA® version 12.0 software was used to calculate pooled odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
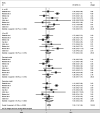
Results: Eight case-control studies qualified for inclusion in the meta-analysis. These studies included 1215 cases and 936 control subjects. There was no significant association between the SLC6A4 gene L/S polymorphism and PAH risk in the total population (LL versus SS: OR 1.83, 95% CI 0.95, 3.51; LS versus SS: OR 1.37, 95% CI 0.93, 2.02; dominant model: OR 1.38, 95% CI 0.97, 1.97; recessive model: OR 1.54, 95% CI 0.84, 2.83). Subgroup analysis based on study quality scores and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium also showed no significant association.
Conclusion: The findings of this meta-analysis suggest that the SLC6A4 gene L/S polymorphism is unlikely to be related to PAH risk. Well-designed studies with more participants will be required to validate these results.
Keywords: 5-hydroxytryptamine transporter; meta-analysis; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Figures


References
-
- McGoon MD, Benza RL, Escribano-Subias P, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: epidemiology and registries. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 62: D51–D59. - PubMed
-
- Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Respir J 2015; 46: 903–975. - PubMed
-
- Ulrich S, Szamalek-Hoegel J, Hersberger M, et al. Sequence variants in BMPR2 and genes involved in the serotonin and nitric oxide pathways in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: relation to clinical parameters and comparison with left heart disease. Respiration 2010; 79: 279–287. - PubMed
-
- Fink KB, Gothert M. 5-HT receptor regulation of neurotransmitter release. Pharmacol Rev 2007; 59: 360–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

