Elastofibroma dorsi: A case report on an unobserved cause of back pain
- PMID: 32962604
- PMCID: PMC7607953
- DOI: 10.5606/ehc.2020.74955
Elastofibroma dorsi: A case report on an unobserved cause of back pain
Abstract
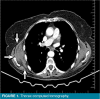
Elastofibroma dorsi (ED) is a rare, benign soft tissue tumor which often occurs in the subscapular region of elderly individuals and shows a female predominance. While many patients remain asymptomatic, ED can cause pain in the periscapular region. The clinical signs of ED are non-specific and variable which can result in misdiagnoses; it is often confused with rotator cuff and cervical spine pathologies. In this article, we present the case of a 78-year-old female patient with persistent back and shoulder pain. The patient was admitted to various clinics over a number of years for diagnostic investigations and treatment. However, the true etiology of back pain was never established and treatments were applied without any positive effect. Finally, when the patient presented to our clinic, a mass was detected in the right subscapular region. Thoracic computed tomography imaging was consistent with a diagnosis of ED. Due to the patient's persistent back pain, surgical excision of the tumor was performed. The pathology report confirmed the diagnosis. This case emphasizes the importance of a thorough examination in patients who may initially only have very subtle signs of the underlying pathology. This case also highlights the importance of re-visiting initial evaluations and differential diagnoses when faced with a difficult case of persistent back and shoulder pain so to avoid misdiagnoses and unnecessary treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elastofibroma dorsi as a cause of shoulder pain or snapping scapula.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001 Jul;(388):200-4. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200107000-00027. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. PMID: 11451120
-
Elastofibroma dorsi: case report and review of the literature.Pan Afr Med J. 2017 Sep 14;28:34. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2017.28.34.13675. eCollection 2017. Pan Afr Med J. 2017. PMID: 29158858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid enlargement of elastofibroma dorsi after physical therapy.Ann Thorac Surg. 2011 May;91(5):1622-4. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2010.10.089. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011. PMID: 21524481
-
[Elastofibroma dorsi: an unusual cause of shoulder pain].Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2009 Nov-Dec;43(5):431-5. doi: 10.3944/AOTT.2009.431. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2009. PMID: 19881325 Turkish.
-
[Elastofibroma dorsi: case report and review of the literature].G Chir. 2006 Oct;27(10):372-6. G Chir. 2006. PMID: 17147850 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Management of Symptomatic Elastofibroma Dorsi: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2022 Sep 14;14(9):e29163. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29163. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36259020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoven-Gondrie ML, IJpma FF, Havenith MG, van Geldere D. Elastofibroma dorsi: a characteristic, benign, subscapular swelling. A569Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2009;153 - PubMed
-
- Järvi OH, Länsimies PH. Subclinical elastofibromas in the scapular region in an autopsy series. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1975;83:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Atik OŞ. Which articles do we prefer to publish. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2018;29:1–1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources