How COVID-19 has changed the unselected medical take: an observational study
- PMID: 32962974
- PMCID: PMC7687303
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.2020-0483
How COVID-19 has changed the unselected medical take: an observational study
Abstract
Introduction: COVID-19 has had a profound effect on the NHS. Little information has been published as to how the unselected medical take has been affected.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed patients who were referred to general medicine during March 2020. We compared clinical outcomes of patients with and without COVID-19.
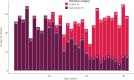
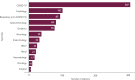
Results: 814 patients were included, comprising 777 unique patients. On average, 26 patients were admitted per day. 38% of admitted patients were suspected of COVID-19, with greater numbers of COVID-19 patients in the second half compared to the first half of the month (p<0.001). Logistic regression analyses showed suspected COVID-19 was an independent predictor for inpatient mortality (odds ratio [OR] = 6.09, p<0.001) and 30-day mortality (OR = 4.66, p<0.001).
Conclusions: COVID-19 patients had worse clinical outcomes and increased healthcare use compared to non-COVID-19 patients. Our study highlights some of the challenges in healthcare provision faced during this pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; medical admissions; medical take.
© 2020 Royal College of Physicians 2020. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Berlin DA, Gulick RM, Martinez FJ. Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020, in press ( 10.1056/NEJMcp2009575). - PubMed
-
- Hunter DJ. Covid-19 and the stiff upper lip - the pandemic response in the United Kingdom. N Engl J Med 2020;382:e31. - PubMed
-
- Stevens S, Pritchard A. Next steps on NHS response to COVID-19: Letter from Sir Simon Stevens and Amanda Pritchard. Available from www.england.nhs.uk/coronavirus/publication/next-steps-on-nhs-response-to... [Accessed 28 May 2020].
-
- Willan J, King AJ, Jeffery K, et al. Challenges for NHS hospitals during Covid-19 epidemic. BMJ 2020;368:m1117. - PubMed
-
- Public Health England Coronavirus (COVID-19) in the UK. https://coronavirus.data.gov.uk/ [Accessed 14 September 2020].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous