Mechanistic study of attenuation of monosodium glutamate mixed high lipid diet induced systemic damage in rats by Coccinia grandis
- PMID: 32963259
- PMCID: PMC7508805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-72076-6
Mechanistic study of attenuation of monosodium glutamate mixed high lipid diet induced systemic damage in rats by Coccinia grandis
Abstract
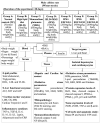
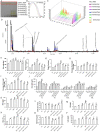
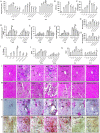
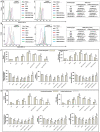
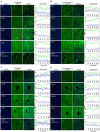
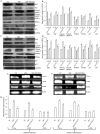
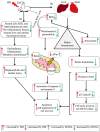
In the context of failure of treatment for non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-mediated systemic damages, recognition of novel and successful characteristic drug to combat these anomalous situations is earnestly required. The present study is aimed to evaluate protective value of ethanol extract of Coccinia grandis leaves (EECGL), naturally occurring medicinal plant, on NAFLD-mediated systemic damage induced by high lipid diet along with monosodium glutamate (HM)-fed rats. Our study uncovered that EECGL significantly ameliorates HM-induced hyperlipidemia, increased lipogenesis and metabolic disturbances (via up regulation of PPAR-α and PPAR-γ), oxidative stress (via reducing the generation of reactive oxygen species and regulating the redox-homeostasis) and inflammatory response (via regulating the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors with concomitant down regulation of NF-kB, iNOS, TNF-α and up regulation of eNOS). Furthermore, EECGL significantly inhibited HM-induced increased population of cells in sub G0/G1 phase, decreased Bcl2 expression and thereby loss of mitochondrial membrane potential with over expression of Bax, p53, p21, activation of caspase 3 and 9 indicated the apoptosis and suppression of cell survival. It is perhaps the first comprehensive study with a mechanistic approach which provides a strong unique strategy for the management of HM-induced systemic damage with effective dose of EECGL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Coccinia grandis against monosodium glutamate induced hepato-cardiac anomalies by inhibiting NF-kB and caspase 3 mediated signalling in rat model.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021 Nov;40(11):1825-1851. doi: 10.1177/09603271211010895. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33887972
-
Coccinia grandis alleviates flavor-enhancing high-lipid diet induced hepatocellular inflammation and apoptosis.J Food Biochem. 2022 May;46(5):e14092. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14092. Epub 2022 Jan 28. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35092065
-
Triterpenoid-rich fraction from Ilex hainanensis Merr. attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high fat diet in rats.Am J Chin Med. 2013;41(3):487-502. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X13500353. Am J Chin Med. 2013. PMID: 23711137
-
Loss of RIP3 initiates annihilation of high-fat diet initialized nonalcoholic hepatosteatosis: A mechanism involving Toll-like receptor 4 and oxidative stress.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Apr;134:23-41. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.12.034. Epub 2018 Dec 30. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30599260
-
Sesamin ameliorates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in rats on a high-fat diet via LXRα and PPARα.Nutr Res. 2016 Sep;36(9):1022-1030. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2016.06.015. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Nutr Res. 2016. PMID: 27632923
Cited by
-
Quercetin inhibits NF-kB and JAK/STAT signaling via modulating TLR in thymocytes and splenocytes during MSG-induced immunotoxicity: an in vitro approach.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 6;51(1):277. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09245-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38319443
-
Dietary food additive monosodium glutamate with or without high-lipid diet induces spleen anomaly: A mechanistic approach on rat model.Open Life Sci. 2022 Jan 29;17(1):22-31. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0004. eCollection 2022. Open Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35128066 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of docetaxel on retinal pigment epithelial cells.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Mar 22;9:670-678. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.03.018. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35433274 Free PMC article.
-
Alarming impact of the excessive use of tert-butylhydroquinone in food products: A narrative review.Toxicol Rep. 2022 May 2;9:1066-1075. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.04.027. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36561954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Black garlic exhibited hepatoprotective effect against monosodium glutamate-induced hepatotoxicity in animal model.Narra J. 2024 Aug;4(2):e799. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i2.799. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39280321 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

