Effects of SoundBite Bone Conduction Hearing Aids on Speech Recognition and Quality of Life in Patients with Single-Sided Deafness
- PMID: 32963516
- PMCID: PMC7495220
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4106949
Effects of SoundBite Bone Conduction Hearing Aids on Speech Recognition and Quality of Life in Patients with Single-Sided Deafness
Abstract
Objectives: To analyze the clinical application of SoundBite bone conduction hearing aids by assessing the improvement of speech recognition and the scores of the benefit scale questionnaire for patients with single-sided deafness (SSD).
Design: Nine patients aged 24 to 61 years with SSD for more than 3 months were enrolled in this study. The patients could understand and repeat Mandarin and have good compliance with the study. The measurements were evaluated before and after one month of wearing hearing aids using the pure tone audiometry threshold, speech recognition in quiet and in noise, and the Glasgow Benefit Inventory (GBI) benefit scale score.
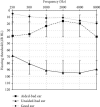
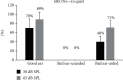
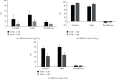
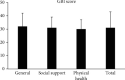
Results: Pure tone audiometry results showed that the average hearing threshold of good ears and bad ears was 11.4 ± 2.6 dB HL and 89.9 ± 6.4 dB HL, respectively. The average hearing threshold of bad ears after wearing hearing aids was 23.5 ± 9.0 dB HL. Statistical analysis showed that the hearing improvement for the bad ears after wearing hearing aids was significant. The speech audiometry results showed that the disyllable word recognition score of the bad ears in quiet increased significantly at 50 dB SPL by 40 ± 12 percentage points and at 65 dB SPL by 71 ± 15 percentage points. As for the speech recognition in noise, when the signal sound came from the bad ear side and the noise from the good ear side (SSSDNAH), the speech recognition score (SRS) significantly increased by 17 ± 6 and 9 ± 4 at a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of -2 dB and -5 dB, respectively, after wearing the hearing aids. When the signal sound came from the front of the patient and the noise from the bad ear side (S0NSSD), the SRS scores were reduced by 5 ± 5 and 7 ± 5 percentage points at SNR equal to -2 dB and -5 dB, which was significantly different from that before wearing the hearing aids. When the signal and noise both came from the front of the patients (S0N0), the SRS was not significantly increased by 5 ± 4 percentage points at SNR equal to -2 dB compared to before wearing hearing aids. However, the SRS was significantly increased by 5 ± 2 percentage points at SNR equal to -5 dB compared to before wearing hearing aids. The average total GBI score was 31 ± 12 for the nine patients, with an average score of 32 ± 10, 31 ± 8, and 30 ± 7 for general conditions, social support, and physical health, respectively. The results of the questionnaires showed that patients' quality of life was improved after wearing SoundBite bone conduction hearing aids.
Conclusions: SoundBite bone conduction hearing aids are a good choice for patients with SSD, as it could improve the speech recognition ability of patients both in a quiet and noisy environment and improves the quality of life after wearing hearing aids.
Copyright © 2020 Qiong Luo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implantable Devices for Single-Sided Deafness and Conductive or Mixed Hearing Loss: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020 Mar 6;20(1):1-165. eCollection 2020. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020. PMID: 32194878 Free PMC article.
-
[Preliminary audiological evaluation of the SoundBite bone conduction devices in adults with single-sided deafness].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 May 7;56(5):478-486. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20200602-00465. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34011002 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Bone-Anchored Hearing Devices for Single-Sided Deafness: A New Preoperative Evaluation Protocol and Widening of Indications Proposal.Audiol Neurootol. 2023;28(3):194-201. doi: 10.1159/000528412. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Audiol Neurootol. 2023. PMID: 36626873
-
Functional Results and Subjective Benefit of a Transcutaneous Bone Conduction Device in Patients With Single-Sided Deafness.Otol Neurotol. 2015 Aug;36(7):1151-6. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000791. Otol Neurotol. 2015. PMID: 26111077 Clinical Trial.
-
Multicentric study on surgical information and early safety and performance results with the Bonebridge BCI 602: an active transcutaneous bone conduction hearing implant.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Apr;280(4):1565-1579. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07792-y. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36625869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brazilian Society of Otology task force - single sided deafness - recommendations based on strength of evidence.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jan-Feb;91(1):101514. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101514. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39378663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-Sided Deafness and Hearing Rehabilitation Modalities: Contralateral Routing of Signal Devices, Bone Conduction Devices, and Cochlear Implants.Brain Sci. 2024 Jan 20;14(1):99. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14010099. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38275519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Intervention effects of bone conduction hearing aids in patients with single-sided deafness and asymmetric hearing loss].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Nov;37(11):927-933. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.11.014. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37905490 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

