Removal of Heavy Metal Ion Using Polymer-Functionalized Activated Carbon: Aspects of Environmental Economic and Chemistry Education
- PMID: 32963883
- PMCID: PMC7492870
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8887488
Removal of Heavy Metal Ion Using Polymer-Functionalized Activated Carbon: Aspects of Environmental Economic and Chemistry Education
Abstract
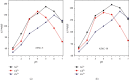
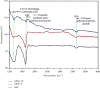
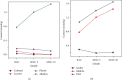
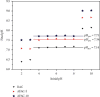
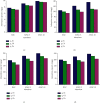
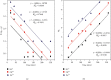
Numerous countries have shown signs of environmental pollution to prioritize economic growth and benefits, leading to seriously contaminated waters. This work indicated the method to synthesize a green material, which could remove contaminants to protect the natural environment. The porosity and functionality effects of amine-functionalized activated carbon (AFAC) enhanced the removal of toxic heavy metals (THMs) in aqueous solution. The raw activated carbon (RAC) was thermally modified with ultrahigh pure nitrogen (UHPN) at 500°C and 1000°C and then amine-functionalized with coupling agent of aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APS). They were denoted as AFAC-5 and AFAC-10, respectively. The data showed an enhanced metal adsorption capacity of the AFACs, because the modification produced more desired porosity and increased amine functional groups. AFAC-10, modified at a higher temperature, showed much higher THM adsorption capacity than AFAC-5, modified at a lower temperature, and RAC. The adsorption capacity decreased in the following order: Ni > Cd > Zn, which was in good agreement with the increasing electronegativity and ionic potential and the decreasing atomic radius. The maximum THM adsorption capacity of AFAC-10 for Ni, Cd, and Zn was 242.5, 226.9, and 204.3 mg/g, respectively.
Copyright © 2020 Hoang Thu Ha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Nguyen T. M. T., Do T. P. T., Hoang T. S., et al. Adsorption of anionic surfactants onto alumina: characteristics, mechanisms, and application for heavy metal removal. International Journal of Polymer Science. 2018;2018:11. doi: 10.1155/2018/2830286.2830286 - DOI
-
- Nguyen T. D., Le H. B., Dong T. O., Pham T. D. Determination of fluoroquinolones in pharmaceutical formulations by extractive spectrophotometric methods using ion-pair complex formation with bromothymol blue. Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry. 2018;2018:11. doi: 10.1155/2018/8436948.8436948 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pham T. D., Kobayashi M., Adachi Y. Adsorption of polyanion onto large alpha alumina beads with variably charged surface. Advances in Physical Chemistry. 2014;2014:9. doi: 10.1155/2014/460942.460942 - DOI
-
- Vu C. M., Nguyen V. H., Vu Thi H., Jin C. W., Nguyen D. D. Hybrid material based on TiO2, CuBTC, and magnetic particles as a novel photocatalyst for MB removal. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology. In press. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

