The impact of disease severity and duration on cost, early retirement and ability to work in rheumatoid arthritis in Europe: an economic modelling study
- PMID: 32964180
- PMCID: PMC7494042
- DOI: 10.1093/rap/rkaa041
The impact of disease severity and duration on cost, early retirement and ability to work in rheumatoid arthritis in Europe: an economic modelling study
Abstract
Objective: RA is a progressive, chronic autoimmune disease. We summarize the impact of disease activity as measured by the DAS in 28 joints (DAS28-CRP scores) and pain on productivity and ability to work using the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment questionnaire (WPAI) scores, in addition to the impact of disease duration on the ability to work.
Methods: Data were drawn from the Burden of RA across Europe: a Socioeconomic Survey (BRASS), a European cross-sectional study in RA. Analyses explored associations between DAS28-CRP score and disease duration with stopping work because of RA, and regression analyses assessed impacts of pain and DAS28-CRP on early retirement and WPAI.
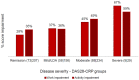
Results: Four hundred and seventy-six RA specialist clinicians provided information on 4079 adults with RA, of whom 2087 completed the patient survey. Severe disease activity was associated with higher rates of stopping work or early retirement attributable to RA (21%) vs moderate/mild disease (7%) or remission (8%). Work impairment was higher in severe (67%) or moderate RA (45%) compared with low disease activity [LDA (37%)] or remission (28%). Moreover, patients with severe (60%) or moderate pain (48%) experienced increased work impairment [mild (34%) or no pain (19%)]. Moderate to severe pain is significant in patients with LDA (35%) or remission (22%). A statistically significant association was found between severity, duration and pain vs work impairment, and between disease duration vs early retirement.
Conclusion: Results demonstrate the high burden of RA. Furthermore, subjective domains, such as pain, could be as important as objective measures of RA activity in affecting the ability to work.
Keywords: health economics; management; outcome measures; pain assessment; quality of life; rheumatoid arthritis.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of rheumatoid arthritis on quality of life, work productivity and resource utilisation: an observational, cross-sectional study in Brazil.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013 May-Jun;31(3):334-40. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23324808
-
Validity of the work productivity and activity impairment questionnaire--general health version in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):R177. doi: 10.1186/ar3141. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20860837 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of response with etanercept-methotrexate therapy in patients with moderately active rheumatoid arthritis in Central and Eastern Europe in the PRESERVE study.Clin Rheumatol. 2013 Sep;32(9):1275-81. doi: 10.1007/s10067-013-2240-4. Epub 2013 May 11. Clin Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23666316 Clinical Trial.
-
European multicentre pilot survey to assess vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis patients and early development of a new Patient Reported Outcome questionnaire (D-PRO).Autoimmun Rev. 2017 May;16(5):548-554. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Autoimmun Rev. 2017. PMID: 28279841 Review.
-
Sarilumab for Previously-Treated Moderate or Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal.Pharmacoeconomics. 2018 Dec;36(12):1427-1437. doi: 10.1007/s40273-018-0677-7. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018. PMID: 29882210 Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between the Quality of Life Domains with Anthropometric and Adiposity Indices in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study from a Single Centre in Erbil-Iraq.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2023 Aug 28;35(2):247-254. doi: 10.31138/mjr.230828.jaa. eCollection 2024 Jun. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 39211015 Free PMC article.
-
Upper extremity joint tenderness as a practical indicator for assessing presenteeism in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A cross-sectional observational study.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 5;20(6):e0318047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318047. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40471982 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for targeted therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Feb 17;8(1):68. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01331-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36797236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural and iatrogenic ocular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review.Int Ophthalmol. 2022 Feb;42(2):689-711. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-02058-8. Epub 2021 Nov 21. Int Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 34802085 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Phytochemicals Unlocks New Avenues in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 16;26(14):6813. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146813. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D. et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1316–22. - PubMed
-
- Lundkvist J, Kastäng F, Kobelt G.. The burden of rheumatoid arthritis and access to treatment: health burden and costs. Eur J Health Econ 2008;8:49–60. - PubMed
-
- European Commission. Musculoskeletal problems and functional limitation. 2003. https://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_projects/2000/monitoring/fp_monitoring_20...
-
- Morse A. Services for people with rheumatoid arthritis. Report by the Comptroller and Auditor General. HC 823 Session 2008–2009. 15 July 2009. National Audit Office. Stationery Office. London, 2009. https://www.nao.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2009/07/0809823.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
