Overview of bariatric and metabolic endoscopy interventions
- PMID: 32964206
- PMCID: PMC7488893
- DOI: 10.1177/2631774520935239
Overview of bariatric and metabolic endoscopy interventions
Abstract
The rise of endoscopic techniques allowing weight loss offers an attractive alternative to surgical interventions in Western countries where the obesity epidemic has risen dramatically. Endoscopists are well positioned to manage obesity given their broad-based medical knowledge, understanding of gastrointestinal physiology, and training in endoscopic technique. The field of bariatric and metabolic endoscopy has permitted the development of several efficacious and safe technologies. This review focuses on techniques and devices used for endoscopic management of obesity, as well as the fundamental justifications to offer those therapies to obese patients.
Keywords: bariatric; endobariatric therapy; endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty.
© The Author(s), 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Michel Kahaleh has done consulting work for Boston Scientific, Interscope Med, and Abbvie. He has received research grants from Boston Scientific, Emcision, Conmed, Pinnacle, Cook, Gore, Merit, and Olympus. The other authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
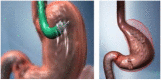
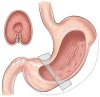
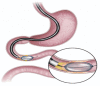
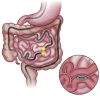
References
-
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2015-2016. NCHS Data Brief 2017; 288: 1–8. - PubMed
-
- Fock KM, Khoo J. Diet and exercise in management of obesity and overweight. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013; 28(Suppl. 4): 59–63. - PubMed
-
- Aronne LJ, Wadden TA, Peterson C, et al. Evaluation of phentermine and topiramate versus phentermine/topiramate extended-release in obese adults. Obesity 2013; 21: 2163–2171. - PubMed
-
- Torgerson JS, Hauptman J, Boldrin MN, et al. XENical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects (XENDOS) study: a randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in obese patients. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 155–161. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

