The genetic basis for the inverse relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia
- PMID: 32965087
- PMCID: PMC7667353
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1483
The genetic basis for the inverse relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia
Abstract
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis is a common autoimmune disease and schizophrenia is a relatively common and debilitating neurological disorder. There are several common features between rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia. The inverse relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia has been replicated in several studies. Despite evidence for an inverse epidemiological relationship and negative correlations for risk between rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia, there are no biological data that directly support this inverse relationship.
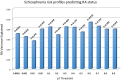
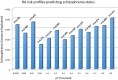
Materials and methods': We meta-analyzed the genome-wide association studies to investigate the shared association loci between rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia at the genome-wide scale. Rheumatoid arthritis- and schizophrenia-associated loci in most recent genome-wide association studies of rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia were tested. Genetic risk score analysis was also conducted to investigate the collective contribution of schizophrenia risk loci to rheumatoid arthritis risk.
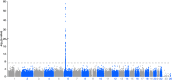
Results: Rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia meta-genome-wide association study showed a significant peak at the major histocompatibility complex locus on chromosome 6 in both rheumatoid arthritis-schizophrenia meta-genome-wide association study and inverted meta-genome-wide association study datasets. Testing rheumatoid arthritis- and schizophrenia-associated loci outside the human leukocyte antigen region showed no association with both rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia at a genome-wide level of significance. Weighted genetic risk scores showed no evidence for a statistically significant association between rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia.
Conclusion: The finding of our study is consistent with the role of the major histocompatibility complex locus in the genetic correlation between rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia, and suggests that either schizophrenia has an autoimmune basis and/or rheumatoid arthritis has an active neurological component.
© 2020 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identifying shared genetic loci and common risk genes of rheumatoid arthritis associated with three autoimmune diseases based on large-scale cross-trait genome-wide association studies.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 12;14:1160397. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1160397. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37377963 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci.Nat Genet. 2010 Jun;42(6):508-14. doi: 10.1038/ng.582. Epub 2010 May 9. Nat Genet. 2010. PMID: 20453842 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis identifies nine new loci associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the Japanese population.Nat Genet. 2012 Mar 25;44(5):511-6. doi: 10.1038/ng.2231. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 22446963
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: identifying and characterising polymorphisms using rat models.Dis Model Mech. 2016 Oct 1;9(10):1111-1123. doi: 10.1242/dmm.026435. Dis Model Mech. 2016. PMID: 27736747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Schizophrenia, rheumatoid arthritis and natural resistance genes.Schizophr Res. 1997 Jun 20;25(3):177-81. doi: 10.1016/s0920-9964(97)00023-6. Schizophr Res. 1997. PMID: 9264173 Review.
Cited by
-
Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial with rituximab for psychotic disorder in adults (RCT-Rits).BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 23;23(1):771. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05250-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37872497 Free PMC article.
-
Schizophrenia and Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetic Scenery: Potential Non-HLA Genes Involved in Both Diseases Relationship.Yale J Biol Med. 2024 Sep 30;97(3):281-295. doi: 10.59249/FBOT5313. eCollection 2024 Sep. Yale J Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39351328 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the multifaceted role of RASGRP1 in disease: immune, neural, metabolic, and oncogenic perspectives.Cell Cycle. 2024 Mar;23(6):722-746. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2024.2366009. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Cell Cycle. 2024. PMID: 38865342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal RasGRP1 Expression in the Post-Mortem Brain and Blood Serum of Schizophrenia Patients.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 18;12(2):328. doi: 10.3390/biom12020328. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204828 Free PMC article.
-
Case-based Insights into Managing Co-existing Rheumatoid Arthritis and Schizophrenia.Indian J Psychol Med. 2024 Feb 27:02537176241226928. doi: 10.1177/02537176241226928. Online ahead of print. Indian J Psychol Med. 2024. PMID: 39564344 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Altamura, A. C. , Buoli, M. , & Pozzoli, S. (2020). Role of immunological factors in the pathophysiology and diagnosis of bipolar disorder: comparison with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 68, 21–36. - PubMed
-
- Allebeck, P. , Rodvall, Y. , & Wistedt, B. (1985). Incidence of rheumatoid arthritis among patients with schizophrenia, affective psychosis and neurosis. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 71, 615–619. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, J. A. (1980). Schizophrenia and physical disease: a preliminary analysis of the data from the Oxford Record Linkage Study In Lancaster H. G. (Ed.), The Biochemistry of Schizophrenia and Addiction. Search of a Common Factor, (pp. 297‐318). Dordrecht, the Netherlands: MTP.
-
- Benros, M. E. , Pedersen, M. G. , Rasmussen, H. , Eaton, W. W. , Nordentoft, M. , & Mortensen, P. B. (2014). A nationwide study on the risk of autoimmune diseases in individuals with a personal or a family history of schizophrenia and related psychosis. American Journal of Psychiatry, 171(2), 218–226. 10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13010086 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen, S.‐J. , Chao, Y.‐L. , Chen, C.‐Y. , Chang, C.‐M. , Wu, E.‐H. , Wu, C.‐S. , … Tsai, H.‐J. (2012). Prevalence of autoimmune diseases in in‐patients with schizophrenia: nationwide population‐based study. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 200(5), 374–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

