Comparison of different prediction models for the indication of implanted cardioverter defibrillator in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 32965795
- PMCID: PMC7755004
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.13019
Comparison of different prediction models for the indication of implanted cardioverter defibrillator in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Aims: Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is associated with a high risk of sudden cardiac death. Three different prediction models for the indication of implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) are now available: the 5 year ARVC risk score, the International Task Force Consensus (ITFC) criteria, and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) criteria. We compared these three prediction models in a validation cohort of patients with definite ARVC.
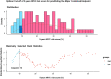
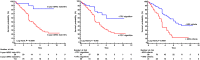
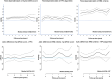
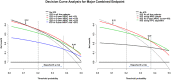
Methods and results: In a cohort of 140 patients with definite ARVC, the 5 year ARVC risk score and the ITFC and HRS criteria were compared for the prediction of a major combined endpoint of sudden cardiac death, appropriate ICD intervention, resuscitated cardiac arrest, and sustained ventricular tachycardia. During the follow-up, 65 major events occurred. The 5 year ARVC risk score with a threshold >10%, derived from the maximally selected rank statistic, predicted 62 (95%) events [odds ratio (OR) 9.1, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2.6-32, P = 0.0006], the ITFC criteria 53 (81%, OR 4.8, 95% CI 2.2-10.3, P = 0.0001), and the HRS criteria 29 (45%, OR 4.2, 95% CI 1.9-9.3, P = 0.0003). At the analysis of decision curve for ICD implantation, a 5 year ARVC risk score >10% showed a greater net benefit than the ITFC and HRS criteria over a wide range of threshold probability of events. Finally, at multivariate analysis, the 5 year ARVC risk score >10% was the only independent predictor of major events.
Conclusions: The 5 year score with a threshold of >10% was more effective for predicting events than the ITFC and HRS criteria.
Keywords: 5 year ARVC risk score; Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy; Heart Rhythm Society criteria; International Task Force Consensus; Prognosis.
© 2020 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Sen‐Chowdhry S, Syrris P, Prasad SK, Hughes SE, Merrifield R, Ward D, Pennell DJ, McKenna WJ. Left‐dominant arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: an under‐recognized clinical entity. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008; 52: 2175–2187. - PubMed
-
- Bennett RG, Haqqani HM, Berruezo A, Della Bella P, Marchlinski FE, Hsu CJ, Kumar S. Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy in 2018–2019: ARVC/ALVC or both? Heart Lung Circ 2019; 28: 164–177. - PubMed
-
- Corrado D, Wichter T, Link MS, Hauer RN, Marchlinski FE, Anastasakis A, Bauce B, Basso C, Brunckhorst C, Tsatsopoulou A, Tandri H, Paul M, Schmied C, Pelliccia A, Duru F, Protonotarios N, Estes NM 3rd, McKenna WJ, Thiene G, Marcus FI, Calkins H. Treatment of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: an international task force consensus statement. Circulation 2015; 132: 441–453. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cadrin‐Tourigny J, Bosman LP, Nozza A, Wang W, Tadros R, Bhonsale A, Bourfiss M, Fortier A, Lie ØH, Saguner AM, Svensson A, Andorin A, Tichnell C, Murray B, Zeppenfeld K, van den Berg MP, Asselbergs FW, Wilde AAM, Krahn AD, Talajic M, Rivard L, Chelko S, Zimmerman SL, Kamel IR, Crosson JE, Judge DP, Yap SC, van der Heijden JF, Tandri H, Jongbloed JDH, Guertin MC, van Tintelen JP, Platonov PG, Duru F, Haugaa KH, Khairy P, Hauer RNW, Calkins H, Te Riele ASJM, James CA. A new prediction model for ventricular arrhythmias in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 2019; 40: 1850–1858. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

