Mutations on COVID-19 diagnostic targets
- PMID: 32966857
- PMCID: PMC7502284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.09.028
Mutations on COVID-19 diagnostic targets
Abstract
Effective, sensitive, and reliable diagnostic reagents are of paramount importance for combating the ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic when there is neither a preventive vaccine nor a specific drug available for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It will cause a large number of false-positive and false-negative tests if currently used diagnostic reagents are undermined. Based on genotyping of 31,421 SARS-CoV-2 genome samples collected up to July 23, 2020, we reveal that essentially all of the current COVID-19 diagnostic targets have undergone mutations. We further show that SARS-CoV-2 has the most mutations on the targets of various nucleocapsid (N) gene primers and probes, which have been widely used around the world to diagnose COVID-19. To understand whether SARS-CoV-2 genes have mutated unevenly, we have computed the mutation rate and mutation h-index of all SARS-CoV-2 genes, indicating that the N gene is one of the most non-conservative genes in the SARS-CoV-2 genome. We show that due to human immune response induced APOBEC mRNA (C > T) editing, diagnostic targets should also be selected to avoid cytidines. Our findings might enable optimally selecting the conservative SARS-CoV-2 genes and proteins for the design and development of COVID-19 diagnostic reagents, prophylactic vaccines, and therapeutic medicines. AVAILABILITY: Interactive real-time online Mutation Tracker.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

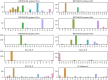

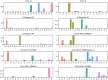
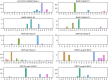
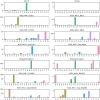


References
-
- WHO . 2020. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report-185 Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019) Situation Reports.
-
- Chan J.F.-W., Yip C.C.-Y., To K.K.W., Tang T.H.-C., Wong S.C.-Y., Leung K.-H., Fung A.Y.-F., Ng A.C.-K., Zou Z., Tsoi H.-W. Improved molecular diagnosis of COVID-19 by the novel, highly sensitive and specific COVID-19-rdrp/hel real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay validated in vitro and with clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020;58(5) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Udugama B., Kadhiresan P., Kozlowski H.N., Malekjahani A., Osborne M., Li V.Y., Chen H., Mubareka S., Gubbay J., Chan W.C. Diagnosing COVID-19: the disease and tools for detection. ACS Nano. 2020;14(4):3822–3835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

