Exenatide and Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 32966971
- PMCID: PMC7677996
- DOI: 10.1159/000510255
Exenatide and Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular outcomes in clinical trials with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients have shown that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist can have a beneficial effect on the kidney. This trial aimed to assess the effects of exenatide on renal outcomes in patients with T2DM and diabetic kidney disease (DKD).
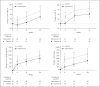
Methods: We performed a randomized parallel study encompassing 4 general hospitals. T2DM patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m2 and macroalbuminuria, defined as 24-h urinary albumin excretion rate (UAER) >0.3 g/24 h were randomized 1:1 to receive exenatide twice daily plus insulin glargine (intervention group) or insulin lispro plus glargine (control group) for 24 weeks. The primary outcome was the UAER percentage change from the baseline after 24 weeks of intervention. The rates of hypoglycemia, adverse events (AEs), and change in eGFR during the follow-up were measured as safety outcomes.
Results: Between March 2016 and April 2019, 92 patients were randomized and took at least 1 dose of the study drug. The mean age of the participants was 56 years. At baseline, the median UAER was 1,512.0 mg/24 h and mean eGFR was 70.4 mL/min/1.73 m2. After 24 weeks of treatment, the UAER percentage change was significantly lower in the intervention group than in the control group (p = 0.0255). Moreover, the body weight declined by 1.3 kg in the intervention group (the difference between the 2 groups was 2.7 kg, p = 0.0001). Compared to the control group, a lower frequency of hypoglycemia and more gastrointestinal AEs were observed in the intervention group.
Conclusion: Exenatide plus insulin glargine treatment for 24 weeks resulted in a reduction of albuminuria in T2DM patients with DKD.
Keywords: Albuminuria; Diabetic kidney disease; Exenatide; Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; Type 2 diabetes.
The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang L, Long J, Jiang W, Shi Y, He X, Zhou Z, et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N Engl J Med. 2016 Sep;375((9)):905–6. - PubMed
-
- Wen CP, Chang CH, Tsai MK, Lee JH, Lu PJ, Tsai SP, et al. Diabetes with early kidney involvement may shorten life expectancy by 16 years. Kidney Int. 2017 Aug;92((2)):388–96. - PubMed
-
- Yamanouchi M, Furuichi K, Hoshino J, Toyama T, Hara A, Shimizu M, et al. Nonproteinuric versus proteinuric phenotypes in diabetic kidney disease: a propensity score-matched analysis of a nationwide, biopsy-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2019 May;42((5)):891–902. - PubMed
-
- Yang JK, Wang YY, Liu C, Shi TT, Lu J, Cao X, et al. Urine proteome specific for eye damage can predict kidney damage in patients with type 2 diabetes: a case-control and a 5.3-year prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2017 Feb;40((2)):253–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

