Evaluation of three-dimensional acromiohumeral distance in the standing position and comparison with its conventional measuring methods
- PMID: 32967710
- PMCID: PMC7510276
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-020-01935-9
Evaluation of three-dimensional acromiohumeral distance in the standing position and comparison with its conventional measuring methods
Abstract
Background: Narrowing of the acromiohumeral distance (AHD) implies a rotator cuff tear. However, conventional AHD measurements using two-dimensional (2D) imaging or with the patient in the supine position might differ from that while standing during daily activity. This study aimed to evaluate the three-dimensional (3D) actual distance between the acromion and humeral head in the standing position and compare the AHD values with those obtained using conventional measuring methods.
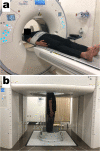
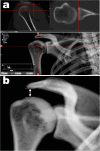
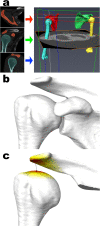
Methods: Computed tomography (CT) images of 166 shoulders from 83 healthy volunteers (31 male and 52 female; mean age 40.1 ± 5.8 years; age range, 30-49 years) were prospectively acquired in the supine and standing positions using conventional and upright CT scanners, respectively. The minimum distance between the acromion and humeral head on the 3D surface models was considered as the 3D AHD. We measured the 2D AHD on anteroposterior digitally reconstructed radiographs. The AHD values were compared between the supine and standing positions and between the 2D and 3D measurements.
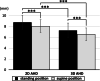
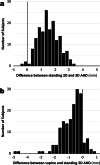
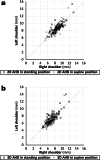
Results: The mean values of 2D AHD were 8.8 ± 1.3 mm (range, 5.9-15.4 mm) in the standing position and 8.1 ± 1.2 mm (range, 5.3-14.3 mm) in the supine position. The mean values of 3D AHD were 7.3 ± 1.4 mm (range, 4.7-14.0 mm) in the standing position and 6.6 ± 1.2 mm (range, 4.4-13.7 mm) in the supine position. The values of 3D AHD were significantly lower than those of 2D AHDs in both the standing and supine positions (P < 0.001). The values of 2D and 3D AHDs were significantly lower in the supine position than in the standing position (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: This study evaluated the 3D AHD of normal shoulders in the standing position using an upright CT scanner. The present results indicated that assessments in the supine position can underestimate the value of the AHD compared with those made in the standing position and that assessments using 2D analysis can overestimate the value.
Keywords: Acromiohumeral distance; Acromiohumeral interval; Digitally reconstructed radiographs; Normal shoulder; Position; Upright computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
Masahiro Jinzaki has received a grant from Canon Medical Systems. However, Canon Medical Systems was not involved in the design and conduct of the study; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data; or in the preparation, review, and approval of the manuscript. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

