Adipocytes: active facilitators in epithelial ovarian cancer progression?
- PMID: 32967712
- PMCID: PMC7513299
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-020-00718-4
Adipocytes: active facilitators in epithelial ovarian cancer progression?
Abstract
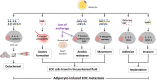
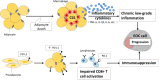
There is growing evidence that adipocytes play important roles in the progression of multiple cancers. Moreover, in obesity, adipocytes alter their original functions and contribute to the metabolic and inflammatory changes of adipose tissue microenvironment, which can further enhance tumor development. At present, the roles of adipocytes in the pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) are far from being fully elucidated. Herein, we summarized the recent advances in understanding the roles of adipocytes in EOC progression. Adipocytes, close neighbors of EOC tissue, promote EOC growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis through adipokine secretion, metabolic remodeling and immune microenvironment modulation. Moreover, adipocytes are important therapeutic targets and may work as useful anticancer drug delivery depot for EOC treatment. Furthermore, adipocytes also act as a therapeutic obstacle for their involvement in EOC treatment resistance. Hence, better characterization of the adipocytes in EOC microenvironment and the crosstalk between adipocytes and EOC cells may provide insights into EOC progression and suggest novel therapeutic opportunities.
Keywords: Adipocytes; Cancer progression; Epithelial ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adipocyte derived exosomes promote cell invasion and challenge paclitaxel efficacy in ovarian cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Sep 16;22(1):443. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01806-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39285292 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of SphK1 by adipocytes mediates epithelial ovarian cancer cell proliferation.J Ovarian Res. 2021 May 1;14(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13048-021-00815-y. J Ovarian Res. 2021. PMID: 33931106 Free PMC article.
-
TRIP13 promotes proliferation and invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer cells through Notch signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jan;23(2):522-529. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201901_16864. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30720159
-
Adipocyte Microenvironment in Ovarian Cancer: A Critical Contributor?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 22;24(23):16589. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316589. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38068912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current insights into the metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer - hopes and hurdles.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Aug;43(4):515-538. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00513-9. Epub 2020 May 16. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 32418122 Review.
Cited by
-
Telomere length as a predictor of therapy response and survival in patients diagnosed with ovarian carcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 29;10(13):e33525. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33525. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39050459 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on anti-ovarian cancer mechanism of miRNA regulating tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1050917. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1050917. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multicellular signalling network of ovarian cancer metastases.Clin Transl Med. 2021 Nov;11(11):e633. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.633. Clin Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34841720 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin/FNDC5 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of epithelial ovarian cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022 Sep;306(3):841-850. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06427-1. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 35156135
-
Metastatic Voyage of Ovarian Cancer Cells in Ascites with the Assistance of Various Cellular Components.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 15;23(8):4383. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084383. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

