Functional evidence that Activin/Nodal signaling is required for establishing the dorsal-ventral axis in the annelid Capitella teleta
- PMID: 32967906
- PMCID: PMC7522025
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.189373
Functional evidence that Activin/Nodal signaling is required for establishing the dorsal-ventral axis in the annelid Capitella teleta
Abstract
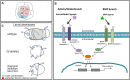
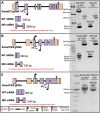
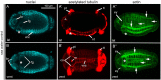
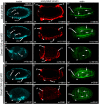
The TGF-β superfamily comprises two distinct branches: the Activin/Nodal and BMP pathways. During development, signaling by this superfamily regulates a variety of embryological processes, and it has a conserved role in patterning the dorsal-ventral body axis. Recent studies show that BMP signaling establishes the dorsal-ventral axis in some mollusks. However, previous pharmacological inhibition studies in the annelid Capitella teleta, a sister clade to the mollusks, suggests that the dorsal-ventral axis is patterned via Activin/Nodal signaling. Here, we determine the role of both the Activin/Nodal and BMP pathways as they function in Capitella axis patterning. Antisense morpholino oligonucleotides were targeted to Ct-Smad2/3 and Ct-Smad1/5/8, transcription factors specific to the Activin/Nodal and BMP pathways, respectively. Following microinjection of zygotes, resulting morphant larvae were scored for axial anomalies. We demonstrate that the Activin/Nodal pathway of the TGF-β superfamily, but not the BMP pathway, is the primary dorsal-ventral patterning signal in Capitella These results demonstrate variation in the molecular control of axis patterning across spiralians, despite sharing a conserved cleavage program. We suggest that these findings represent an example of developmental system drift.
Keywords: Annelid; Axes formation; BMP; Morpholino; Spiralian; TGF-β.
© 2020. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures








References
-
- Amiel A. R., Henry J. Q. and Seaver E. C. (2013). An organizing activity is required for head patterning and cell fate specification in the polychaete annelid Capitella teleta: new insights into cell-cell signaling in Lophotrochozoa. Dev. Biol. 379, 107-122. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.04.011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

