Structural and molecular basis for the substrate positioning mechanism of a new PL7 subfamily alginate lyase from the arctic
- PMID: 32967968
- PMCID: PMC7705320
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015106
Structural and molecular basis for the substrate positioning mechanism of a new PL7 subfamily alginate lyase from the arctic
Abstract
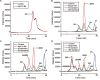
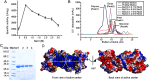
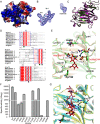
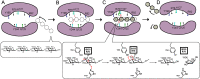
Alginate lyases play important roles in alginate degradation in the ocean. Although a large number of alginate lyases have been characterized, little is yet known about those in extremely cold polar environments, which may have unique mechanisms for environmental adaptation and for alginate degradation. Here, we report the characterization of a novel PL7 alginate lyase AlyC3 from Psychromonas sp. C-3 isolated from the Arctic brown alga Laminaria, including its phylogenetic classification, catalytic properties, and structure. We propose the establishment of a new PM-specific subfamily of PL7 (subfamily 6) represented by AlyC3 based on phylogenetic analysis and enzymatic properties. Structural and biochemical analyses showed that AlyC3 is a dimer, representing the first dimeric endo-alginate lyase structure. AlyC3 is activated by NaCl and adopts a novel salt-activated mechanism; that is, salinity adjusts the enzymatic activity by affecting its aggregation states. We further solved the structure of an inactive mutant H127A/Y244A in complex with a dimannuronate molecule and proposed the catalytic process of AlyC3 based on structural and biochemical analyses. We show that Arg82 and Tyr190 at the two ends of the catalytic canyon help the positioning of the repeated units of the substrate and that His127, Tyr244, Arg78, and Gln125 mediate the catalytic reaction. Our study uncovers, for the first time, the amino acid residues for alginate positioning in an alginate lyase and demonstrates that such residues involved in alginate positioning are conserved in other alginate lyases. This study provides a better understanding of the mechanisms of alginate degradation by alginate lyases.
Keywords: Arctic; PL7 family; algae; alginate lyase; enzyme degradation; enzyme mechanism; metabolism; subfamily; substrate positioning.
© 2020 Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Usov A. I., Bilan M. I., and Klochkova N. G. (1995) Polysaccharides of algae: 48. Polysaccharide composition of several calcareous red algae: isolation of alginate from Corallina pilulifera P. et R. (Rhodophyta, Corallinaceae). Bot. Mar. 38, 43–51 10.1515/botm.1995.38.1-6.43 - DOI
-
- Gorin P. A. J., and Spencer J. F. T. (1966) Exocellular alginic acid from Azotobacter vinelandii. Can. J. Chem. 44, 993–998 10.1139/v66-147 - DOI
-
- Linker A., and Jones R. S. (1966) A new polysaccharide resembling alginic acid isolated from Pseudomonads. J. Biol. Chem. 241, 3845–3851 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

