14-3-3ζ-TRAF5 axis governs interleukin-17A signaling
- PMID: 32968020
- PMCID: PMC7547158
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2008214117
14-3-3ζ-TRAF5 axis governs interleukin-17A signaling
Abstract
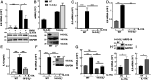
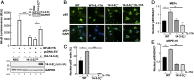
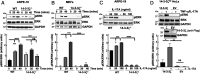
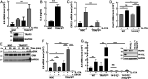
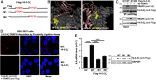
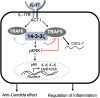
IL-17A is a therapeutic target in many autoimmune diseases. Most nonhematopoietic cells express IL-17A receptors and respond to extracellular IL-17A by inducing proinflammatory cytokines. The IL-17A signal transduction triggers two broad, TRAF6- and TRAF5-dependent, intracellular signaling pathways to produce representative cytokines (IL-6) and chemokines (CXCL-1), respectively. Our limited understanding of the cross-talk between these two branches has generated a crucial gap of knowledge, leading to therapeutics indiscriminately blocking IL-17A and global inhibition of its target genes. In previous work, we discovered an elevated expression of 14-3-3 proteins in inflammatory aortic disease, a rare human autoimmune disorder with increased levels of IL-17A. Here we report that 14-3-3ζ is essential for IL-17 signaling by differentially regulating the signal-induced IL-6 and CXCL-1. Using genetically manipulated human and mouse cells, and ex vivo and in vivo rat models, we uncovered a function of 14-3-3ζ. As a part of the molecular mechanism, we show that 14-3-3ζ interacts with several TRAF proteins; in particular, its interaction with TRAF5 and TRAF6 is increased in the presence of IL-17A. In contrast to TRAF6, we found TRAF5 to be an endogenous suppressor of IL-17A-induced IL-6 production, an effect countered by 14-3-3ζ. Furthermore, we observed that 14-3-3ζ interaction with TRAF proteins is required for the IL-17A-induced IL-6 levels. Together, our results show that 14-3-3ζ is an essential component of IL-17A signaling and IL-6 production, an effect that is suppressed by TRAF5. To the best of our knowledge, this report of the 14-3-3ζ-TRAF5 axis, which differentially regulates IL-17A-induced IL-6 and CXCL-1 production, is unique.
Keywords: 14-3-3ζ; IL-17A; TRAF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ishigame H. et al., Differential roles of interleukin-17A and -17F in host defense against mucoepithelial bacterial infection and allergic responses. Immunity 30, 108–119 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Leonardi C. et al., Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 1190–1199 (2012). - PubMed
-
- van Baarsen L. G. et al., Heterogeneous expression pattern of interleukin 17A (IL-17A), IL-17F and their receptors in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis: Possible explanation for nonresponse to anti-IL-17 therapy? Arthritis Res. Ther. 16, 426 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pacheco-Lugo L. et al., Plasma cytokines as potential biomarkers of kidney damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 28, 34–43 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

