Heme oxygenase 1 protects human colonocytes against ROS formation, oxidative DNA damage and cytotoxicity induced by heme iron, but not inorganic iron
- PMID: 32968051
- PMCID: PMC7511955
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02950-8
Heme oxygenase 1 protects human colonocytes against ROS formation, oxidative DNA damage and cytotoxicity induced by heme iron, but not inorganic iron
Abstract
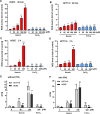
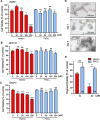
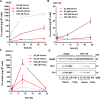
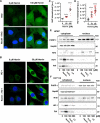
The consumption of red meat is probably carcinogenic to humans and is associated with an increased risk to develop colorectal cancer (CRC). Red meat contains high amounts of heme iron, which is thought to play a causal role in tumor formation. In this study, we investigated the genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of heme iron (i.e., hemin) versus inorganic iron in human colonic epithelial cells (HCEC), human CRC cell lines and murine intestinal organoids. Hemin catalyzed the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and induced oxidative DNA damage as well as DNA strand breaks in both HCEC and CRC cells. In contrast, inorganic iron hardly affected ROS levels and only slightly increased DNA damage. Hemin, but not inorganic iron, caused cell death and reduced cell viability. This occurred preferentially in non-malignant HCEC, which was corroborated in intestinal organoids. Both hemin and inorganic iron were taken up into HCEC and CRC cells, however with differential kinetics and efficiency. Hemin caused stabilization and nuclear translocation of Nrf2, which induced heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and ferritin heavy chain (FtH). This was not observed after inorganic iron treatment. Chemical inhibition or genetic knockdown of HO-1 potentiated hemin-triggered ROS generation and oxidative DNA damage preferentially in HCEC. Furthermore, HO-1 abrogation strongly augmented the cytotoxic effects of hemin in HCEC, revealing its pivotal function in colonocytes and highlighting the toxicity of free intracellular heme iron. Taken together, this study demonstrated that hemin, but not inorganic iron, induces ROS and DNA damage, resulting in a preferential cytotoxicity in non-malignant intestinal epithelial cells. Importantly, HO-1 conferred protection against the detrimental effects of hemin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemoglobin and hemin induce DNA damage in human colon tumor cells HT29 clone 19A and in primary human colonocytes.Mutat Res. 2006 Feb 22;594(1-2):162-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.08.006. Epub 2005 Oct 13. Mutat Res. 2006. PMID: 16226281
-
Inhibition of replication of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by hemin is highly dependent on heme oxygenase-1, but independent of iron in MARC-145 cells.Antiviral Res. 2014 May;105:39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Antiviral Res. 2014. PMID: 24583029
-
Hemin induces an iron-dependent, oxidative injury to human neuron-like cells.J Neurosci Res. 2003 Jul 1;73(1):113-21. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10633. J Neurosci Res. 2003. PMID: 12815715
-
A Dual Role of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 21;20(1):39. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010039. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30583467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Functions, Inductions, Regulations, and Signaling.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021 Jun;52(2):454-461. doi: 10.1007/s12029-021-00587-0. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33484436 Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabidiol modulation of oxidative stress and signalling.Neuronal Signal. 2021 Aug 24;5(3):NS20200080. doi: 10.1042/NS20200080. eCollection 2021 Sep. Neuronal Signal. 2021. PMID: 34497718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of HO-1 and Its Crosstalk with Oxidative Stress in Cancer Cell Survival.Cells. 2021 Sep 13;10(9):2401. doi: 10.3390/cells10092401. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Selenium Nanocomposite Protects the Mouse Brain from Oxidative Injury Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Feb 4;16:775-788. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S293681. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33574665 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of heart disease.Front Physiol. 2024 Sep 10;15:1450656. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1450656. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39318361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cre-Recombinase Induces Apoptosis and Cell Death in Enterocyte Organoids.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;11(8):1452. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081452. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892654 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

