Ancestral sequence reconstruction produces thermally stable enzymes with mesophilic enzyme-like catalytic properties
- PMID: 32968141
- PMCID: PMC7511310
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-72418-4
Ancestral sequence reconstruction produces thermally stable enzymes with mesophilic enzyme-like catalytic properties
Abstract
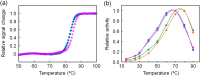
Enzymes have high catalytic efficiency and low environmental impact, and are therefore potentially useful tools for various industrial processes. Crucially, however, natural enzymes do not always have the properties required for specific processes. It may be necessary, therefore, to design, engineer, and evolve enzymes with properties that are not found in natural enzymes. In particular, the creation of enzymes that are thermally stable and catalytically active at low temperature is desirable for processes involving both high and low temperatures. In the current study, we designed two ancestral sequences of 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase by an ancestral sequence reconstruction technique based on a phylogenetic analysis of extant homologous amino acid sequences. Genes encoding the designed sequences were artificially synthesized and expressed in Escherichia coli. The reconstructed enzymes were found to be slightly more thermally stable than the extant thermophilic homologue from Thermus thermophilus. Moreover, they had considerably higher low-temperature catalytic activity as compared with the T. thermophilus enzyme. Detailed analyses of their temperature-dependent specific activities and kinetic properties showed that the reconstructed enzymes have catalytic properties similar to those of mesophilic homologues. Collectively, our study demonstrates that ancestral sequence reconstruction can produce a thermally stable enzyme with catalytic properties adapted to low-temperature reactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Substitutions of coenzyme-binding, nonpolar residues improve the low-temperature activity of thermophilic dehydrogenases.Biochemistry. 2011 Oct 11;50(40):8583-93. doi: 10.1021/bi200925f. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21894900
-
Establishment of mesophilic-like catalytic properties in a thermophilic enzyme without affecting its thermal stability.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 27;9(1):9346. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45560-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31249343 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the low-temperature adaptation of an enzyme as studied through ancestral sequence reconstruction.Protein Sci. 2025 Mar;34(3):e70071. doi: 10.1002/pro.70071. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 39968914 Free PMC article.
-
Helping proteins come in from the cold: 5 burning questions about cold-active enzymes.BBA Adv. 2023 Nov 27;5:100104. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2023.100104. eCollection 2024. BBA Adv. 2023. PMID: 38162634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo versus in vitro screening or selection for catalytic activity in enzymes and abzymes.Mol Biotechnol. 1997 Feb;7(1):37-55. doi: 10.1007/BF02821543. Mol Biotechnol. 1997. PMID: 9163721 Review.
Cited by
-
An Ancestry Perspective of the Evolution of PBS1 Proteins in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 25;22(13):6819. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136819. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201937 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-Art Biocatalysis.ACS Cent Sci. 2021 Jul 28;7(7):1105-1116. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00273. Epub 2021 Jun 25. ACS Cent Sci. 2021. PMID: 34345663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering functional thermostable proteins using ancestral sequence reconstruction.J Biol Chem. 2022 Oct;298(10):102435. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102435. Epub 2022 Aug 27. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36041629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strangers in a foreign land: 'Yeastizing' plant enzymes.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;17(9):e14525. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14525. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39222378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
uPIC-M: Efficient and Scalable Preparation of Clonal Single Mutant Libraries for High-Throughput Protein Biochemistry.ACS Omega. 2021 Nov 2;6(45):30542-30554. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04180. eCollection 2021 Nov 16. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34805683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chapman J, Ismail AE, Dinu CZ. Industrial applications of enzymes: Recent advances, techniques, and outlooks. Catalysts. 2018;8:238. doi: 10.3390/catal8060238. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

