Diagnostic value of VDBP and miR-155-5p in diabetic nephropathy and the correlation with urinary microalbumin
- PMID: 32968443
- PMCID: PMC7500046
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9214
Diagnostic value of VDBP and miR-155-5p in diabetic nephropathy and the correlation with urinary microalbumin
Abstract
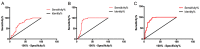
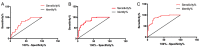
This study explored the diagnostic and therapeutic significance of vitamin D binding protein (VDBP) and miR-155-5p for diabetic nephropathy and the correlation with urinary microalbumin. A total of 145 patients with type 2 diabetes who attended the Hwamei hospital were selected as research objects and assigned to diabetic nephropathy group (DN group) and diabetes group according to whether they suffered from diabetic nephropathy (DN). The expression levels of urine VDBP and serum miR-155-5p in the two groups were detected, and the correlation between urinary microalbumin (mAlb), serum cystatin C (Cys C) and 24-h urinary protein was analyzed. The predictive value of single and joint detection of urinary VDBP and serum miR-155-5p for DN onset and poor prognosis was analyzed. In DN patients, urine VDBP and serum miR-155-5p were highly expressed, and urine VDBP, serum miR-155-5p and mAlb, Cys C and 24-h urine protein were positively correlated (P<0.05). Moreover, the joint detection of urine VDBP and serum miR-155-5p was more valuable in diagnosis and poor prognosis prediction of DN patients than its single detection. Urine VDBP and serum miR-155-5p have good diagnostic value for DN, but their joint diagnostic value is higher, and their expression levels are all related to mAlb of DN patients, which may be used as new biological indicators for diagnosis and disease assessment.
Keywords: VDBP; correlation; diabetic nephropathy; diagnostic value; miR-155-5p; urinary microalbumin.
Copyright: © Bai et al.
Figures
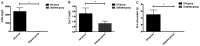

Similar articles
-
Elevated urinary level of vitamin D-binding protein as a novel biomarker for diabetic nephropathy.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Feb;7(2):411-416. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1426. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24396416 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D-Binding Protein Clearance Ratio Is Significantly Associated with Glycemic Status and Diabetes Complications in a Predominantly Vitamin D-Deficient Population.J Diabetes Res. 2018 May 20;2018:6239158. doi: 10.1155/2018/6239158. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 29888290 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Exosomal miRNA Signature in Type II Diabetic Nephropathy Patients.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 1;11(3):e0150154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150154. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26930277 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of the combined measurement of serum hcy, serum cys C, and urinary microalbumin in type 2 diabetes mellitus with early complicating diabetic nephropathy.ISRN Endocrinol. 2013 Sep 18;2013:407452. doi: 10.1155/2013/407452. eCollection 2013. ISRN Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 24159393 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Proteome Analysis for Detection of Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Arterial Hypertension [Internet].Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2015 Sep 17. Executive Summary of Final Report No. D13-01. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2015 Sep 17. Executive Summary of Final Report No. D13-01. PMID: 29144688 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased Serum Insulin Receptor Messenger RNA Level in H. pylori IgG Seropositive Type 2 Diabetic Patients.Biomark Insights. 2024 Nov 4;19:11772719241296619. doi: 10.1177/11772719241296619. eCollection 2024. Biomark Insights. 2024. PMID: 39502307 Free PMC article.
-
Network analysis identifies circulating miR-155 as predictive biomarker of type 2 diabetes mellitus development in obese patients: a pilot study.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 9;13(1):19496. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46516-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37945677 Free PMC article.
-
Tribulus terrestris L. protects glomerular endothelial cells via the miR155-H2AC6 interaction network in hypertensive renal injury.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Nov;9(21):1626. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5641. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34926670 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Molecular Networks and Regulatory MicroRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Multiomics Integration and Interactomics Study.JMIR Bioinform Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 23;3(1):e32437. doi: 10.2196/32437. JMIR Bioinform Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 38935970 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D Binding Protein and Renal Injury in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 9;9:829490. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.829490. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35757319 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
