New insights into the role of nanotechnology in microbial food safety
- PMID: 32968610
- PMCID: PMC7483685
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-020-02409-9
New insights into the role of nanotechnology in microbial food safety
Abstract
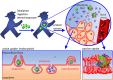
Today, the role of nanotechnology in human life is undeniable as a broad range of industries, particularly food and medicine sectors, have been dramatically influenced. Nanomaterials can contribute to food safety by forming new nano-sized ingredients with modified physicochemical characteristics. Nanotechnologies can inhibit the growth of food spoilage microorganisms by recruiting novel and unique agents that are involved in removal of microbes from foods or prevent adhesion of microbial cells to food surfaces. Hence, nanotechnology could be considered as a high-potential tool in food packaging, safety, and preservation. Moreover, the prevention of biofilm formation by disturbing the attachment of bacteria to the food surface is another useful nanotechnological approach. Recently, nanoparticle-based biosensors have been designed and developed to detect the food-borne pathogens and hazardous substances through complicated mechanisms. During the past half-century, many methods such as freeze-drying and spray drying have been employed for increasing the viability in food industries; however, the other novel approaches such as encapsulation methods have also been developed. Admittedly, some beneficial bacteria such as probiotics bring diverse benefits for human health if only they are in a sufficient number and viability in the food products and gastrointestinal tract (GI). Encapsulation of these valuable microbial strains by nanoparticles improves the survival of probiotics under harsh conditions such as extreme levels of temperature, pH, and salinity during the processing of food products and within the GIT tract. The survival and effectiveness of encapsulated microorganisms depends on different factors including function of cell wall components in bacteria and type of coating materials. This review aims to broadly explore the potential of different aspects of nanotechnology in food industry, especially for packaging, preservation, safety, and viability.
Keywords: Encapsulation; Food safety; Nanotechnology; Nutraceuticals; Probiotics; Viability.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Introducing nano/microencapsulated bioactive ingredients for extending the shelf-life of food products.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020 Aug;282:102210. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102210. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020. PMID: 32726708 Review.
-
Nanotechnology-based approaches applied to nutraceuticals.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Mar;12(3):485-499. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00960-3. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 33738677 Review.
-
Nanoparticle applications in food - a review.Food Funct. 2023 Mar 20;14(6):2544-2567. doi: 10.1039/d2fo02180c. Food Funct. 2023. PMID: 36799219 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Update on Nanotechnology in Functional Food Developments: Recent Updates, Challenges, and Future Perspectives.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025;19(2):241-256. doi: 10.2174/1872210517666230825100347. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 37904558 Review.
-
Microencapsulation: a pragmatic approach towards delivery of probiotics in gut.J Microencapsul. 2021 Sep;38(6):437-458. doi: 10.1080/02652048.2021.1949062. Epub 2021 Jul 19. J Microencapsul. 2021. PMID: 34192983
Cited by
-
Campylobacter control strategies at postharvest level.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 27;33(13):2919-2936. doi: 10.1007/s10068-024-01644-7. eCollection 2024 Oct. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39220305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neuroprotective Effects of Curcumin Nanoparticles on The Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in The Rats-The Roles of The Protein Kinase RNA-Like ER Kinase/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase and Transcription Factor EB proteins.Cell J. 2024 Jan 31;26(1):62-69. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2023.1995696.1257. Cell J. 2024. PMID: 38351730 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Biotechnological Approaches Applied for Marine Hydrocarbon Spills Remediation.Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 25;10(7):1289. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071289. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging trends in nano-sensors: A new frontier in food safety and quality assurance.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 12;11(1):e41181. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41181. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39807502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Application of Nanomaterials as Treatments for Bacterial Infectious Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 12;13(11):1913. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111913. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aabdallah M, Bayoumy A, Ibrahim A. Antimicrobial activity and synergistic antimicrobial potential of silver nanoparticles against microbial contaminants isolated from pharmaceutical production areas. Res J Appl Biotech. 2019;5:86–98.
-
- Ali MA, Eldin TAS, Moghazy GMEL, Tork IM, Omara II. Detection of E. coli O157: H7 in feed samples using gold nanoparticles sensor. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2014;3:697–708.
-
- Anema SG. Age gelation, sedimentation, and creaming in UHT Milk: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2019;18:140–166. - PubMed
-
- Aruguete DM, Kim B, Hochella MF, Ma Y, Cheng Y, Hoegh A, Liu J, Pruden A. Antimicrobial nanotechnology: it’s potential for the effective management of microbial drug resistance and implications for research needs in microbial nanotoxicology. Enviro Sci Process Impacts. 2013;15:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Bao C, Jiang P, Chai J, Jiang Y, Li D, Bao W, Liu B, Liu B, Norde W, Li Y. The delivery of sensitive food bioactive ingredients: Absorption mechanisms, influencing factors, encapsulation techniques and evaluation models. Food Res Int. 2019;120:130–140. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

