Inhibition of ERK or Akt ameliorates intimal hyperplasia via up-regulation of Cx37 and down-regulation of Cx43 in balloon injury rat model
- PMID: 32968622
- PMCID: PMC7487390
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-20-345
Inhibition of ERK or Akt ameliorates intimal hyperplasia via up-regulation of Cx37 and down-regulation of Cx43 in balloon injury rat model
Abstract
Background: Connexins (Cxs) are reported to participate in atherosclerosis associated intimal hyperplasia (IH), while their function involved in the balloon injury (BI) induced IH and restenosis is less reported.
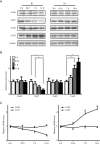
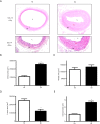
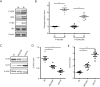
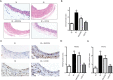
Methods: Forty-eight male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly assigned to not injured (NI) group and BI group, which were further administrated with ERK-inhibitor U0216 and Akt-inhibitor MIK2206. Western blot and RT-PCR were utilized to detect the expression of Cx30, Cx37, Cx40, and Cx43 at 6 hours, 24 hours, 7 days, and 14 days post-surgery. H&E staining and related intima area, media area, and luminal area measurement were applied to indicate neointima formation and IH. ERK and Akt phosphorylation levels and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunostaining were also detected.
Results: Among the four Cxs detected, Cx37 showed down-regulated, and Cx43 showed up-regulated temporal expression pattern in BI rats with confirmed neointima formation. Up-regulated p-ERK (P<0.01) and p-Akt (P<0.01) can be detected in BI rats compared with NI rats. Meanwhile, U0216 and MIK2206 can significantly reduce Cx43 expression and increase CX37 expression accompanied with reduced neointima formation and PCNA staining (P<0.05 or P<0.01) in BI rats.
Conclusions: ERK or Akt inhibition can alleviate BI-induced IH via up-regulation of Cx37 and down-regulation of Cx43.
Keywords: Akt; Cx37; Cx43; ERK; intimal hyperplasia (IH).
2020 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/cdt-20-345). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Connexin37 reduces smooth muscle cell proliferation and intimal hyperplasia in a mouse model of carotid artery ligation.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Jun 1;113(7):805-816. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx079. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28449099
-
Increased connexin43 expression in human saphenous veins in culture is associated with intimal hyperplasia.J Vasc Surg. 2005 Jun;41(6):1043-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.02.036. J Vasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 15944608
-
[Co-overexpression of human tissue kallikrein 1 and human metalloproteinase 1 tissue inhibitor inhibits neointima formation in the rat artery after balloon angioplasty].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2016 May 24;44(5):436-42. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2016.05.014. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27220581 Chinese.
-
Human urine kininogenase attenuates balloon-induced intimal hyperplasia in rabbit carotid artery through transforming growth factor β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway.J Vasc Surg. 2016 Oct;64(4):1074-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.04.433. Epub 2015 Jun 6. J Vasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 26054589
-
The cyclolignan picropodophyllin attenuates intimal hyperplasia after rat carotid balloon injury by blocking insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling.J Vasc Surg. 2007 Jul;46(1):108-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2007.02.066. J Vasc Surg. 2007. PMID: 17606126
Cited by
-
MMP-9 Deletion Attenuates Arteriovenous Fistula Neointima through Reduced Perioperative Vascular Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 21;22(11):5448. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115448. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34064140 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1/SMOC2/AKT and ERK axis regulates proliferation, migration, and fibroblast to myofibroblast transformation in lung fibroblast, contributing with the asthma progression.Hereditas. 2021 Dec 8;158(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s41065-021-00213-w. Hereditas. 2021. PMID: 34876240 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
