Exogenous endothelial progenitor cells reached the deficient region of acute cerebral ischemia rats to improve functional recovery via Bcl-2
- PMID: 32968626
- PMCID: PMC7487376
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-20-329
Exogenous endothelial progenitor cells reached the deficient region of acute cerebral ischemia rats to improve functional recovery via Bcl-2
Abstract
Background: As discovered in our previous study, autologous endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) protect against acute focal ischemia rat via the promotion of angiogenesis. However, it is unknown whether the EPCs that reached the deficient region were transplanted ones or the products of other auto-conversion cells they had promoted. This study aimed to gather direct evidence for determining if exogenous transplanted EPCs directly participate in angiogenesis in ischemic areas and attempted to clarify the related mechanism.
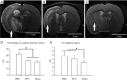
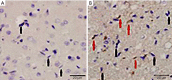
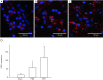
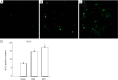
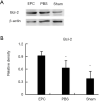
Methods: First, EPCs were extracted in vitro from male rats, which were characterized by uptake of fluorescently labeled acetylated low-density lipoprotein (ac-LDL) intake and Ulex europaeus agglutinin (UEA-1) and subsequently introduced to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) female rats for 7 days after ischemia surgery. The EPC-treated animals received approximately 1×106 cells, while the control animals received phosphate buffered saline (PBS). The animals behavior function recovery were by a rotarod (TOR) test, while infarct volume was assessed by brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). CD31 antibody was used to determine the presence of EPCs in the ischemic zone, and sex-determining region Y (SRY) gene in-situ hybridization (ISH) traced the EPC process. In addition, immunohistochemistry and Western blot were used to assess B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) expression in the ischemic brain.
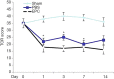
Results: Behavior tests and MRI of all ischemic stroke groups on postoperative day 14 indicated that EPCs were more effective in behavior function recovery and reducing infarct volume and gliosis status than the control group. Cluster of differentiation (CD31) immunofluorescent staining and SRY gene ISH demonstrated that EPCs yielded a better outcome in both angiogenesis and exogenous cell homing status. We also observed increased Bcl-2 distribution and higher plasma Bcl-2 levels in the EPC-treated group compared to the control group.
Conclusions: Our results provide direct evidence that exogenous EPCs can participate in angiogenesis to improve neurological outcome and revascularization directly after stroke, with Bcl-2 playing an important role in this process.
Keywords: Bcl-2; Stroke; angiogenesis; behavior; endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs).
2020 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/cdt-20-329). All authors report grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, outside the submitted work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adiponectin-Transfected Endothelial Progenitor Cells Have Protective Effects After 2-Hour Middle-Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Neurol. 2021 Mar 3;12:630681. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.630681. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33746885 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the potential of endothelial progenitor cells as a treatment following ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 8;13:940682. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.940682. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36158970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial progenitor cells improve functional recovery in focal cerebral ischemia of rat by promoting angiogenesis via VEGF.J Clin Neurosci. 2018 Sep;55:116-121. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2018.07.011. Epub 2018 Jul 21. J Clin Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30041898
-
Human umbilical cord-derived endothelial progenitor cells promote growth cytokines-mediated neorevascularization in rat myocardial infarction.Chin Med J (Engl). 2009 Mar 5;122(5):548-55. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009. PMID: 19323906
-
In situ Reprogramming as a Pro-Angiogenic Inducer to Rescue Ischemic Tissues.Pulse (Basel). 2024 May 29;12(1):58-65. doi: 10.1159/000538075. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Pulse (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39022557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Mononuclear Cells in the Treatment of Neurological Diseases: Knowns and Unknowns.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;43(7):3211-3250. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01377-x. Epub 2023 Jun 25. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37356043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiponectin-Transfected Endothelial Progenitor Cells Have Protective Effects After 2-Hour Middle-Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Neurol. 2021 Mar 3;12:630681. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.630681. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33746885 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the potential of endothelial progenitor cells as a treatment following ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 8;13:940682. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.940682. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36158970 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
