Performance of cardiovascular magnetic resonance strain in patients with acute myocarditis
- PMID: 32968629
- PMCID: PMC7487388
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-20-221
Performance of cardiovascular magnetic resonance strain in patients with acute myocarditis
Abstract
Background: To explore the value of myocardial strain derived from cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) feature tracking in evaluating left ventricular function in acute myocarditis and its relationship with the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE).
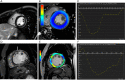
Methods: A total of 115 cases of clinically suspected acute myocarditis, confirmed by CMR, were collected from two centers and divided into groups with reduced and preserved ejection fraction (EF). Fifty normal volunteers were enrolled as the control group. The myocardial strain analysis was based on feature tracking imaging (FTI).
Results: Compared with the control group, the group with myocarditis and preserved EF showed an increased peak ejecting rate (PER), end diastolic volume (EDV), end systolic volume (ESV), stroke volume (SV), EDV index (EDVi), ESV index (ESVi), SV index (SVi) and decreased strain indices. In patient with myocarditis, the group with reduced EF showed increased EDV, ESV, LGE, LGE% and decreased strain indices compared to the group with preserved EF. EF showed good correlation with LGE, PSC, PSSRC (r>0.6). Peak strain circumferential (PSC) showed good correlation with LGE (r=0.62). The AUC of PSC was optimal to detect early left ventricular dysfunction in myocarditis patient with preserved EF using a cutoff of -19.72% (sensitivity of 68% and specificity of 88%).
Conclusions: Myocardial strain analysis using CMR FTI can provide information about early ventricular dysfunction in myocarditis patient with preserved EF. PSC showed best diagnostic performance, and correlated with LGE.
Keywords: Myocarditis; feature tracking; late gadolinium enhancement (LGE); left ventricular function; magnetic resonance imaging.
2020 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/cdt-20-221). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Strain in Suspected Myocarditis With Preserved LV-EF: A Comparison Between Patients With Negative and Positive Late Gadolinium Enhancement Findings.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Apr;55(4):1109-1119. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27873. Epub 2021 Aug 8. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34369030
-
Unveiling the Diagnostic Value of Strain Parameters Across All 4 Cardiac Chambers in Patients With Acute Myocarditis With Varied Ejection Fraction: A Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Feature-Tracking Approach.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Jul 2;13(13):e032781. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.032781. Epub 2024 Jun 27. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38934873 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking myocardial strain analysis in suspected acute myocarditis: diagnostic value and association with severity of myocardial injury.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Mar 28;23(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03201-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 36977995 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of late gadolinium enhancement in cardiac magnetic resonance on the diastolic volume recovery of left ventricle with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.J Thorac Dis. 2014 Jul;6(7):988-94. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.06.37. J Thorac Dis. 2014. PMID: 25093097 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of late gadolinium enhancement in myocarditis and clinically suspected myocarditis: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2020 May;30(5):2616-2626. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06643-5. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32040731
Cited by
-
The association of myocardial strain with cardiac magnetic resonance and clinical outcomes in patients with acute myocarditis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jul 31;10:1121083. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1121083. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37588035 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac cine with compressed sensing real-time imaging and retrospective motion correction for free-breathing assessment of left ventricular function and strain in clinical practice.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Apr 1;13(4):2262-2277. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-596. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37064398 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Speckle Tracking Analysis of Right Ventricle Function in Myocarditis with Preserved Right Ventricular Ejection Fraction.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Sep 25;60(10):1569. doi: 10.3390/medicina60101569. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39459355 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Cardiac Magnetic Resonance-Based Feature Tracking and Deep-Learning Strain Assessment in Patients Hospitalized for Acute Myocarditis.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 31;12(3):1113. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031113. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769762 Free PMC article.
-
Right and left ventricular cardiac magnetic resonance imaging derived peak systolic strain is abnormal in children with myocarditis.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Jan;40(1):139-147. doi: 10.1007/s10554-023-02975-y. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37861812
References
-
- Caforio AL, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E, et al. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J 2013;34:2636-48, 2648a-2648d. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
