Ephrin B2 mediates high glucose induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human aortic endothelial cells
- PMID: 32968633
- PMCID: PMC7487366
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-20-299
Ephrin B2 mediates high glucose induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human aortic endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Previous study revealed that high glucose (HG) induced endothelial cell (EC) damage via endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT). Recent studies suggested the role of Ephrin B2 in mediate ECs damage. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether Ephrin B2 mediates HG-induced EndMT in human aortic ECs (HAECs) and to determine the possible downstream signaling effector.
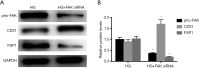
Methods: Primary HAECs were exposed to normal glucose (NG, 5.5 mM), HG (30 mM) and HG+Ephrin B2 small interfering RNA (siRNA), respectively. The pathological changes were investigated by light microscope and confocal microscopy. To study the effects of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation on Ephrin B2 in HAECs, cells were incubated with FAK siRNA in HG group. The expression of EndMT-related markers (CD31 and FSP1), Ephrin B2 and FAK were detected by qRT-PCR and western blot.
Results: The results showed that HG significantly inhibited the expression of CD31 and increased FSP1 compared with NG group. Moreover, Ephrin B2 was increased after HG incubation. Ephrin B2 siRNA attenuated HG-induced expression of EndMT-related markers. Furthermore, HG increased the expression of FAK and phosphorylated FAK (pho-FAK) in HAECs. In contrast, blocking Ephrin B2 could partially attenuate HG-induced FAK activation. And FAK siRNA further inhibited the EndMT-related markers in HAECs treated with HG.
Conclusions: HG-induced EndMT in HAECs might be partially mediated by Ephrin B2 and the downstream FAK pathway.
Keywords: Ephrin B2; endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT); focal adhesion kinase (FAK); high glucose (HG); human aortic endothelial cell (HAEC).
2020 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/cdt-20-299). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



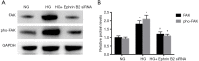

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
