Successes and gaps in the HIV cascade of care of a high HIV prevalence setting in Zimbabwe: a population-based survey
- PMID: 32969602
- PMCID: PMC7513352
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.25613
Successes and gaps in the HIV cascade of care of a high HIV prevalence setting in Zimbabwe: a population-based survey
Abstract
Introduction: Gutu, a rural district in Zimbabwe, has been implementing comprehensive HIV care with the support of Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) since 2011, decentralizing testing and treatment services to all rural healthcare facilities. We evaluated HIV prevalence, incidence and the cascade of care, in Gutu District five years after MSF began its activities.
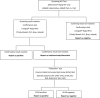
Methods: A cross-sectional study was implemented between September and December 2016. Using multistage cluster sampling, individuals aged ≥15 years living in the selected households were eligible. Individuals who agreed to participate were interviewed and tested for HIV at home. All participants who tested HIV-positive had their HIV-RNA viral load (VL) measured, regardless of their antiretroviral therapy (ART) status, and those not on ART with HIV-RNA VL ≥ 1000 copies/mL had Limiting-Antigen-Avidity EIA Assay for cross-sectional estimation of population-level HIV incidence.
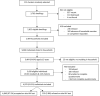
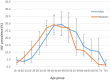
Results: Among 5439 eligible adults ≥15 years old, 89.0% of adults were included in the study and accepted an HIV test. The overall prevalence was 13.6% (95%: Confidence Interval (CI): 12.6 to 14.5). Overall HIV-positive status awareness was 87.4% (95% CI: 84.7 to 89.8), linkage to care 85.5% (95% CI: 82.5 to 88.0) and participants in care 83.8% (95% CI: 80.7 to 86.4). ART coverage among HIV-positive participants was 83.0% (95% CI: 80.0 to 85.7). Overall, 71.6% (95% CI 68.0 to 75.0) of HIV-infected participants had a HIV-RNA VL < 1000 copies/mL. Women achieved higher outcomes than men in the five stages of the cascade of care. Viral Load Suppression (VLS) among participants on ART was 83.2% (95% CI: 79.7 to 86.2) and was not statistically different between women and men (p = 0.98). The overall HIV incidence was estimated at 0.35% (95% CI 0.00 to 0.70) equivalent to 35 new cases/10,000 person-years.
Conclusions: Our study provides population-level evidence that achievement of HIV cascade of care coverage overall and among women is feasible in a context with broad access to services and implementation of a decentralized model of care. However, the VLS was relatively low even among participants on ART. Quality care remains the most critical gap in the cascade of care to further reduce mortality and HIV transmission.
Keywords: ART; HIV; cascade of care; incidence; prevalence; viral suppression.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International AIDS Society.
Figures
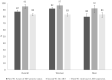
References
-
- Ministry of Health and Child Care (MOHCC) . Zimbabwe Population‐based HIV Impact Assessment (ZIMPHIA) 2016: first report. December 2017.
-
- WHO . Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection. Recommendation for a public health approach. Second edition. 2016. - PubMed
-
- WHO . Progress report 2016: prevent HIV, test and treat all: WHO support for country impact. Whorld Health Organization; 2016.
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS . 90‐90‐90 ‐ An ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Geneva, Switzerland: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2014. [Internet] [cited 2020 Mar 19]. Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2017/90‐90‐90
-
- Zimbabwe National Statisitics Agency . Census 2012 Provincial Report Masvingo, Zimbabwe. 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

