Ultrasound Elastography for Lung Disease Assessment
- PMID: 32970595
- PMCID: PMC8544928
- DOI: 10.1109/TUFFC.2020.3026536
Ultrasound Elastography for Lung Disease Assessment
Abstract
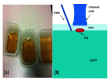
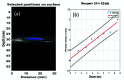
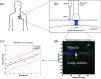
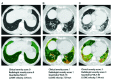
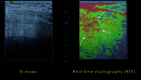
Ultrasound elastography (US-E) is a noninvasive, safe, cost-effective and reliable technique to assess the mechanical properties of soft tissue and provide imaging biomarkers for pathological processes. Many lung diseases such as acute respiratory distress syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and interstitial lung disease are associated with dramatic changes in mechanical properties of lung tissues. Nevertheless, US-E is rarely used to image the lung because it is filled with air. The large difference in acoustic impedance between air and lung tissue results in the reflection of the ultrasound wave at the lung surface and, consequently, the loss of most ultrasound energy. In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in US-E applications in evaluating lung diseases. This article provides a comprehensive review of the technological advances of US-E research on lung disease diagnosis. We introduce the basic principles and major techniques of US-E and provide information on various applications in lung disease assessment. Finally, the potential applications of US-E to the diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia is discussed.
Figures

References
-
- McLaughlin V. V.et al., “ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: A report of the American college of cardiology foundation task force on expert consensus documents and the American heart association: Developed in collaboration with the American college of chest physicians, American thoracic society, Inc., and the pulmonary hypertension association,” Circulation, vol. 119, no. 16, pp. 2250–2294, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Reissig A., Gramegna A., and Aliberti S., “The role of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis and follow-up of community-acquired pneumonia,” Eur. J. Internal Med., vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 391–397, Jul. 2012. - PubMed
-
- Tardella M., Di Carlo M., Carotti M., Filippucci E., Grassi W., and Salaffi F., “Ultrasound B-lines in the evaluation of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis: Cut-off point definition for the presence of significant pulmonary fibrosis,” Medicine, vol. 97, no. 18, p. e0566, May 2018. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

