High Mobility Group Protein 1 and Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 in Schizophrenia and Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Associations With Interleukin-6, Symptom Domains, and Neurocognitive Impairments
- PMID: 32971537
- PMCID: PMC7965081
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbaa136
High Mobility Group Protein 1 and Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 in Schizophrenia and Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Associations With Interleukin-6, Symptom Domains, and Neurocognitive Impairments
Abstract
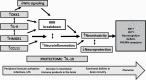
Background: Schizophrenia (SCZ) and treatment-resistant schizophrenia (TRS) are associated with aberrations in immune-inflammatory pathways. Increased high mobility group protein 1 (HMGB1), an inflammatory mediator, and Dickkopf-related protein (DKK1), a Wnt/β-catenin signaling antagonist, affect the blood-brain barrier and induce neurotoxic effects and neurocognitive deficits.
Aim: The present study aims to examine HMGB1 and DDK1 in nonresponders to treatments (NRTT) with antipsychotics (n = 60), partial RTT (PRTT, n = 55), and healthy controls (n = 43) in relation to established markers of SCZ, including interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, and CCL11 (eotaxin), and to delineate whether these proteins are associated with the SCZ symptom subdomains and neurocognitive impairments.
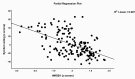
Results: HMGB1, DKK1, IL-6, and CCL11 were significantly higher in SCZ patients than in controls. DKK1 and IL-6 were significantly higher in NRTT than in PRTT and controls, while IL-10 was higher in NRTT than in controls. Binary logistic regression analysis showed that SCZ was best predicted by increased DDK1 and HMGB1, while NRTT (vs PRTT) was best predicted by increased IL-6 and CCL11 levels. A large part of the variance in psychosis, hostility, excitation, mannerism, and negative (PHEMN) symptoms and formal thought disorders was explained by HMGB1, IL-6, and CCL11, while most neurocognitive functions were predicted by HMGB1, DDK1, and CCL11.
Conclusions: The neurotoxic effects of HMGB1, DKK1, IL-6, and CCL11 including the effects on the blood-brain barrier and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway may cause impairments in executive functions and working, episodic, and semantic memory and explain, in part, PHEMN symptoms and a nonresponse to treatment with antipsychotic drugs.
Keywords: cytokines; inflammation; neuro-immune; neurocognition; schizophrenia; treatment resistance.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Schizophrenia. In: World Health Organization. World Health Organization; 2018. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia. Accessed February 4, 2020.
-
- Smith RS, Maes M. The macrophage-T-lymphocyte theory of schizophrenia: additional evidence. Med Hypotheses. 1995;45:135–141. - PubMed
-
- Maes M, Delange J, Ranjan R, et al. Acute phase proteins in schizophrenia, mania and major depression: modulation by psychotropic drugs. Psychiatry Res. 1997;66(1):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Lin A, Kenis G, Bignotti S, et al. The inflammatory response system in treatment-resistant schizophrenia: increased serum interleukin-6. Schizophr Res. 1998;32(1):9–15. - PubMed
-
- Maes M, Bocchio Chiavetto L, Bignotti S, et al. Effects of atypical antipsychotics on the inflammatory response system in schizophrenic patients resistant to treatment with typical neuroleptics. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2000;10(2):119–124. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

