Novel Bis-Ammonium Salts of Pyridoxine: Synthesis and Antimicrobial Properties
- PMID: 32971844
- PMCID: PMC7570726
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184341
Novel Bis-Ammonium Salts of Pyridoxine: Synthesis and Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
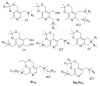
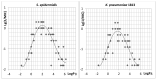
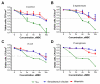
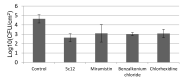
A series of 108 novel quaternary bis-ammonium pyridoxine derivatives carrying various substituents at the quaternary nitrogen's and acetal carbon was synthesized. Thirteen compounds exhibited antibacterial and antifungal activity (minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) 0.25-16 µg/mL) comparable or superior than miramistin, benzalkonium chloride, and chlorhexidine. A strong correlation between the lipophilicity and antibacterial activity was found. The most active compounds had logP values in the range of 1-3, while compounds with logP > 6 and logP < 0 were almost inactive. All active compounds demonstrated cytotoxicity comparable with miramistin and chlorhexidine on HEK-293 cells and were three-fold less toxic when compared to benzalkonium chloride. The antibacterial activity of leading compound 5c12 on biofilm-embedded Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas aeruginosa was comparable or even higher than that of the benzalkonium chloride. In vivo 5c12was considerably less toxic (LD50 1705 mg/kg) than benzalkonium chloride, miramistine, and chlorhexidine at oral administration on CD-1 mice. An aqueous solution of 5c12 (0.2%) was shown to be comparable to reference drugs efficiency on the rat's skin model. The molecular target of 5c12 seems to be a cellular membrane as other quaternary ammonium salts. The obtained results make the described quaternary bis-ammonium pyridoxine derivatives promising and lead molecules in the development of the new antiseptics with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity.
Keywords: antibacterial activity; antifungal activity; antiseptics; biofilms; cytotoxicity; pyridoxine; quaternary ammonium salts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Targeting pathogenic fungi, bacteria and fungal-bacterial biofilms by newly synthesized quaternary ammonium derivative of pyridoxine and terbinafine with dual action profile.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104306. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104306. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33011535
-
Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Novel Quaternary Ammonium Pyridoxine Derivatives.Med Chem. 2015;11(7):656-65. doi: 10.2174/1573406411666150504122930. Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25938426
-
Bis-phosphonium salts of pyridoxine: the relationship between structure and antibacterial activity.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Dec 1;21(23):7330-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.09.056. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24139168
-
Quaternary ammonium salts and their antimicrobial potential: targets or nonspecific interactions?ChemMedChem. 2012 Jan 2;7(1):22-31. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201100404. Epub 2011 Nov 24. ChemMedChem. 2012. PMID: 22113995 Review.
-
Antimicrobial polymeric materials with quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Feb 6;16(2):3626-55. doi: 10.3390/ijms16023626. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25667977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bushy-Tailed Multicationic Quaternary Phosphonium Compounds: Potent Amphiphilic Disinfectants with Promising Therapeutic Indices.ChemMedChem. 2025 Feb 16;20(4):e202400546. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202400546. Epub 2024 Nov 20. ChemMedChem. 2025. PMID: 39448380 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable triazine-derived quaternary ammonium salts as antimicrobial agents.RSC Adv. 2021 Aug 19;11(45):28092-28096. doi: 10.1039/d1ra03455c. eCollection 2021 Aug 16. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35480717 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Synthesis of Biologically Active Quaternary Ammonium Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 24;25(9):4649. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094649. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (QACs) and Ionic Liquids (ILs) as Biocides: From Simple Antiseptics to Tunable Antimicrobials.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 24;22(13):6793. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136793. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Significance of Hydrophobic and Hydrogen Bonding Interaction for Nanoscale Hybridization of Antiseptic Miramistin Molecules with Molybdenum Disulfide Monolayers.Molecules. 2023 Feb 10;28(4):1702. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041702. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Review on Antimicrobial Resistance . Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. Review on AMR, Wellcome Trust, HM Government; London, UK: 2014. [(accessed on 20 July 2020)]. Available online: http://www.jpiamr.eu/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/AMR-Review-Paper-Tacklin....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

