Ultrapotent human antibodies protect against SARS-CoV-2 challenge via multiple mechanisms
- PMID: 32972994
- PMCID: PMC7857395
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abe3354
Ultrapotent human antibodies protect against SARS-CoV-2 challenge via multiple mechanisms
Abstract
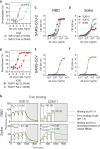
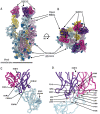
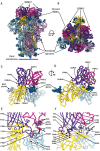
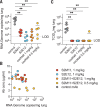
Efficient therapeutic options are needed to control the spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that has caused more than 922,000 fatalities as of 13 September 2020. We report the isolation and characterization of two ultrapotent SARS-CoV-2 human neutralizing antibodies (S2E12 and S2M11) that protect hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 challenge. Cryo-electron microscopy structures show that S2E12 and S2M11 competitively block angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) attachment and that S2M11 also locks the spike in a closed conformation by recognition of a quaternary epitope spanning two adjacent receptor-binding domains. Antibody cocktails that include S2M11, S2E12, or the previously identified S309 antibody broadly neutralize a panel of circulating SARS-CoV-2 isolates and activate effector functions. Our results pave the way to implement antibody cocktails for prophylaxis or therapy, circumventing or limiting the emergence of viral escape mutants.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.-R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.-L., Chen H.-D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.-D., Liu M.-Q., Chen Y., Shen X.-R., Wang X., Zheng X.-S., Zhao K., Chen Q.-J., Deng F., Liu L.-L., Yan B., Zhan F.-X., Wang Y.-Y., Xiao G.-F., Shi Z.-L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579, 270–273 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Zhao X., Huang B., Shi W., Lu R., Niu P., Zhan F., Ma X., Wang D., Xu W., Wu G., Gao G. F., Tan W.; China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team , A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 727–733 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou H., Chen X., Hu T., Li J., Song H., Liu Y., Wang P., Liu D., Yang J., Holmes E. C., Hughes A. C., Bi Y., Shi W., A Novel Bat Coronavirus Closely Related to SARS-CoV-2 Contains Natural Insertions at the S1/S2 Cleavage Site of the Spike Protein. Curr. Biol. 30, 2196–2203.e3 (2020). 10.1016/j.cub.2020.05.023 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drosten C., Günther S., Preiser W., van der Werf S., Brodt H.-R., Becker S., Rabenau H., Panning M., Kolesnikova L., Fouchier R. A. M., Berger A., Burguière A.-M., Cinatl J., Eickmann M., Escriou N., Grywna K., Kramme S., Manuguerra J.-C., Müller S., Rickerts V., Stürmer M., Vieth S., Klenk H.-D., Osterhaus A. D. M. E., Schmitz H., Doerr H. W., Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1967–1976 (2003). 10.1056/NEJMoa030747 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ksiazek T. G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C. S., Zaki S. R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J. A., Lim W., Rollin P. E., Dowell S. F., Ling A.-E., Humphrey C. D., Shieh W.-J., Guarner J., Paddock C. D., Rota P., Fields B., DeRisi J., Yang J.-Y., Cox N., Hughes J. M., LeDuc J. W., Bellini W. J., Anderson L. J.; SARS Working Group , A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1953–1966 (2003). 10.1056/NEJMoa030781 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

