Inborn errors of type I IFN immunity in patients with life-threatening COVID-19
- PMID: 32972995
- PMCID: PMC7857407
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abd4570
Inborn errors of type I IFN immunity in patients with life-threatening COVID-19
Abstract
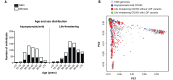
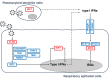
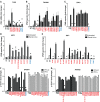
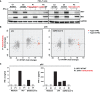
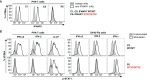
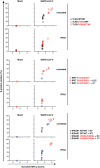
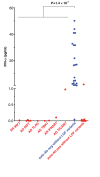
Clinical outcome upon infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) ranges from silent infection to lethal coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We have found an enrichment in rare variants predicted to be loss-of-function (LOF) at the 13 human loci known to govern Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3)- and interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7)-dependent type I interferon (IFN) immunity to influenza virus in 659 patients with life-threatening COVID-19 pneumonia relative to 534 subjects with asymptomatic or benign infection. By testing these and other rare variants at these 13 loci, we experimentally defined LOF variants underlying autosomal-recessive or autosomal-dominant deficiencies in 23 patients (3.5%) 17 to 77 years of age. We show that human fibroblasts with mutations affecting this circuit are vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2. Inborn errors of TLR3- and IRF7-dependent type I IFN immunity can underlie life-threatening COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with no prior severe infection.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

Comment in
-
Susceptibility to severe COVID-19.Science. 2020 Oct 23;370(6515):404-405. doi: 10.1126/science.abe7591. Science. 2020. PMID: 33093097 No abstract available.
-
Marked changes in innate immunity associated with a mild course of COVID-19 in identical twins with athymia and absent circulating T cells.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Feb;147(2):567-568. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.11.007. Epub 2020 Dec 3. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33309039 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Do monogenic inborn errors of immunity cause susceptibility to severe COVID-19?J Clin Invest. 2021 Jul 15;131(14):e149459. doi: 10.1172/JCI149459. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34061775 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- HHSN272201400008C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091707/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI138938/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201800048C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- C0483/MRF_/MRF_/United Kingdom
- R01 AI088364/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135972/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI111825/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93019C00051/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG008956/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135834/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI142733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

