PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers
- PMID: 32973135
- PMCID: PMC7515865
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02998-6
PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers
Abstract
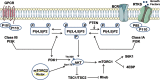
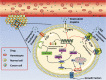
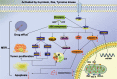
Multidrug resistance (MDR) is the dominant challenge in the failure of chemotherapy in cancers. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is a lipid kinase that spreads intracellular signal cascades and regulates a variety of cellular processes. PI3Ks are considered significant causes of chemoresistance in cancer therapy. Protein kinase B (AKT) is also a significant downstream effecter of PI3K signaling, and it modulates several pathways, including inhibition of apoptosis, stimulation of cell growth, and modulation of cellular metabolism. This review highlights the aberrant activation of PI3K/AKT as a key link that modulates MDR. We summarize the regulation of numerous major targets correlated with the PI3K/AKT pathway, which is further related to MDR, including the expression of apoptosis-related protein, ABC transport and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β), synergism with nuclear factor kappa beta (NF-κB) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and the regulation of glycolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB and GSK-3β pathways in the rat model of cardiopulmonary bypass-related lung injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:747-754. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.125. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29990867
-
Overexpression of Biglycan is Associated with Resistance to Rapamycin in Human WERI-Rb-1 Retinoblastoma Cells by Inducing the Activation of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinases (PI3K)/Akt/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Sep 4;25:6639-6648. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915075. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31483776 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-proliferative effect of RCE-4 from Reineckia carnea on human cervical cancer HeLa cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and NF-κB activation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;389(6):573-84. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1217-7. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26935715
-
Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 May;142(2):164-75. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24333502 Review.
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin module for acute myelogenous leukemia therapy: from bench to bedside.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(19):2009-23. doi: 10.2174/092986707781368423. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17691943 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting miR-21 to Overcome P-glycoprotein Drug Efflux in Doxorubicin-Resistant 4T1 Breast Cancer.Biomater Res. 2024 Oct 21;28:0095. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0095. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39434899 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrion: Main organelle in orchestrating cancer escape from chemotherapy.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Feb;7(2):e1942. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1942. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38151790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DKK1 as a chemoresistant protein modulates oxaliplatin responses in colorectal cancer.Oncogenesis. 2024 Sep 27;13(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41389-024-00537-y. Oncogenesis. 2024. PMID: 39333078 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of microRNA-124 in traumatic brain injury: a comprehensive review.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Nov 28;17:1298508. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1298508. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38034588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting esophageal carcinoma: molecular mechanisms and clinical studies.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 15;5(11):e782. doi: 10.1002/mco2.782. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39415846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sharma A. Chemoresistance in cancer cells: exosomes as potential regulators of therapeutic tumor heterogeneity. Nanomedicine. 2017;12:2137–2148. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Mayea Y, Mir C, Masson F, Paciucci R, LLeonart ME. Insights into new mechanisms and models of cancer stem cell multidrug resistance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020;60:166–180. - PubMed
-
- Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:48–58. - PubMed
-
- DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB. The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab. 2008;7:11–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

