The neuropathic phenotype of the K/BxN transgenic mouse with spontaneous arthritis: pain, nerve sprouting and joint remodeling
- PMID: 32973194
- PMCID: PMC7515905
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-72441-5
The neuropathic phenotype of the K/BxN transgenic mouse with spontaneous arthritis: pain, nerve sprouting and joint remodeling
Abstract
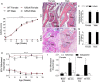
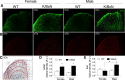
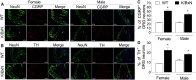
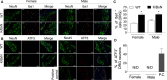
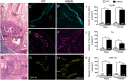
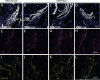
The adult K/BxN transgenic mouse develops spontaneous autoimmune arthritis with joint remodeling and profound bone loss. We report that both males and females display a severe sustained tactile allodynia which is reduced by gabapentin but not the potent cyclooxygenase inhibitor ketorolac. In dorsal horn, males and females show increased GFAP+ astrocytic cells; however, only males demonstrate an increase in Iba1+ microglia. In dorsal root ganglia (DRG), there is an increase in CGRP+, TH+, and Iba1+ (macrophage) labeling, but no increase in ATF3+ cells. At the ankle there is increased CGRP+, TH+, and GAP-43+ fiber synovial innervation. Thus, based on the changes in dorsal horn, DRG and peripheral innervation, we suggest that the adult K/BxN transgenic arthritic mice display a neuropathic phenotype, an assertion consistent with the analgesic pharmacology seen in this animal. These results indicate the relevance of this model to our understanding of the nociceptive processing which underlies the chronic pain state that evolves secondary to persistent joint inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wolfe F, Michaud K, Li T. Sleep disturbance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Evaluation by medical outcomes study and visual analog sleep scales. J. Rheumatol. 2006;33:1942–1951. - PubMed
-
- Sambrook PN. The skeleton in rheumatoid arthritis: Common mechanisms for bone erosion and osteoporosis? J. Rheumatol. 2000;27:2541–2542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

