Serum proteins may facilitate the identification of Kawasaki disease and promote in vitro neutrophil infiltration
- PMID: 32973234
- PMCID: PMC7518260
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-72695-z
Serum proteins may facilitate the identification of Kawasaki disease and promote in vitro neutrophil infiltration
Abstract
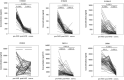
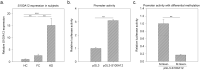
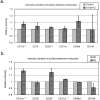
Kawasaki disease (KD) usually affects the children younger than 5 years of age and subsequently causes coronary artery lesions (CALs) without timely identification and treatment. Developing a robust and fast prediction method may facilitate the timely diagnosis of KD, significantly reducing the risk of CALs in KD patients. The levels of inflammatory serum proteins dramatically vary during the onsets of many immune diseases, including in KD. However, our understanding of their pathogenic roles in KD is behind satisfaction. The purpose of this study was to evaluate candidate diagnostic serum proteins and the potential mechanism in KD using iTRAQ gel-free proteomics. We enrolled subjects and conducted iTRAQ gel-free proteomics to globally screen serum proteins followed by specific validation with ELISA. Further in vitro leukocyte trans-endothelial model was also applied to investigate the pathogenesis roles of inflammatory serum proteins. We identified six KD protein biomarkers, including Protein S100-A8 (S100A8), Protein S100-A9 (S100A9), Protein S100-A12 (S100A12), Peroxiredoxin-2 (PRDX2), Neutrophil defensin 1 (DEFA1) and Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 (ORM1). They enabled us to develop a high-performance KD prediction model with an auROC value of 0.94, facilitating the timely identification of KD. Further assays concluded that recombinant S100A12 protein treatment activated neutrophil surface adhesion molecules responsible for adhesion to endothelial cells. Therefore, S100A12 promoted both freshly clinically isolated neutrophils and neutrophil-like cells to infiltrate through the endothelial layer in vitro. Finally, the antibody against S100A12 may attenuate the infiltration promoted by S100A12. Our result demonstrated that evaluating S100A8, S100A9, S100A12, PRDX2, DEFA1 and ORM1 levels may be a good diagnostic tool of KD. Further in vitro study implied that S100A12 could be a potential therapeutic target for KD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
iTRAQ Proteomics Identified the Potential Biomarkers of Coronary Artery Lesion in Kawasaki Disease and In Vitro Studies Demonstrated That S100A4 Treatment Made HCAECs More Susceptible to Neutrophil Infiltration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 23;23(21):12770. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112770. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361563 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical indicators combined with S100A12/TLR2 signaling molecules to establish a new scoring model for coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 12;18(10):e0292653. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292653. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37824465 Free PMC article.
-
S100A12 on circulating endothelial cells surface in children with Kawasaki disease.Pediatr Res. 2010 Aug;68(2):165-8. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181e67ce8. Pediatr Res. 2010. PMID: 20461025
-
S100 proteins in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Mar;502:293-304. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.11.019. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 31794767 Review.
-
S100A12 and the S100/Calgranulins: Emerging Biomarkers for Atherosclerosis and Possibly Therapeutic Targets.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Dec;35(12):2496-507. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.302072. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26515415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deficiency of Acute-Phase Serum Amyloid A Exacerbates Sepsis-Induced Mortality and Lung Injury in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 15;24(24):17501. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417501. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139330 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes Secreted by Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote the Ability of Cell Proliferation and Migration for Keratinocyte.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 26;25(9):4758. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094758. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731977 Free PMC article.
-
iTRAQ Proteomics Identified the Potential Biomarkers of Coronary Artery Lesion in Kawasaki Disease and In Vitro Studies Demonstrated That S100A4 Treatment Made HCAECs More Susceptible to Neutrophil Infiltration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 23;23(21):12770. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112770. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361563 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Adding Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) to Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) among Patients with Rotator Cuff Partial Tear: A Prospective Randomized Comparative Study.J Pers Med. 2024 Jan 10;14(1):83. doi: 10.3390/jpm14010083. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38248784 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Children With Chronic Kidney Disease: Impact of Apolipoprotein C-II and Apolipoprotein C-III.Front Pediatr. 2021 Aug 12;9:706323. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.706323. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34458211 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

