Clinical Presentation of Patients Infected with Coronavirus Disease 19: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32973375
- PMCID: PMC7495523
- DOI: 10.1177/1178633720952076
Clinical Presentation of Patients Infected with Coronavirus Disease 19: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease-19 has been labeled a pandemic by World Health Organization. By virtue of its highly contagious attribution, this virus has spread across over the world and the numbers are still rapidly increasing. Increasing numbers of confirmed cases and mortality rates of coronavirus disease 2019 are occurring in several countries. The aim of this systematic review was to summarize clinical presentations of this newly emerging coronavirus disease.
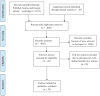
Methods: A systematic review of published articles was conducted using databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar. A search was conducted on 18 to 25 April 2020. Search terms included "novel coronavirus," "2019 novel coronavirus," "Coronavirus disease 2019," "COVID-19," "severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2." The studies published in the English language and their full texts available were included. The eligible study designs were cross-sectional, case-control, cohort, and case series.
Results: Thirty (30) studies which contain 4829 participants were included in this review. From included studies, the age of infected patients were found in range 0.25 to 94 years. The main clinical symptoms of COVID-19 patients were fever (77.6%), cough (64.8%), fatigue (27.2%), dyspnea (21.2%) and sputum production (18.0%).
Conclusion: This systematic review identified that fever, cough, fatigue, and dyspnea were the most common reported clinical features of coronavirus disease 19. Understanding of the clinical spectrum and impact of this novel disease is important for all individuals, especially for healthcare workers to manage and prevent it.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus disease 19; clinical presentation; systematic review.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease, 2020. https://www.who.int. Accessed April 18, 2020.
-
- Zhao W, Yu S, Zha X, et al. Clinical characteristics and durations of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Beijing: a retrospective cohort study. MedRxiv. 2020.
-
- COVID-19. Coronavirus pandemic, April 19, 2020. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/. Accessed April 19, 2020.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

